Why Automated Calibration in Print Inspection Systems is More and More Widely Used
Table of Contents
The printing industry constantly strives to achieve high-quality output while minimizing errors and waste. Automated calibration in print inspection systems has become a critical solution for meeting these objectives. This technology improves precision, ensures consistency and enhances overall operational efficiency, making it indispensable for modern printing inspection.

Importance of Calibration in Print Inspection Systems
Calibration ensures that print inspection systems deliver consistent and accurate results. It aligns the system’s sensors, cameras, and processing units to predefined standards, enabling:
- Color Consistency: Precise reproduction of colors is vital in packaging, branding, and high-quality publications.
- Defect Identification: Detection of misprints, smudges, and alignment issues with minimal false positives.
- Cost-Effective Operations: Reducing waste due to printing errors by identifying issues early in the process.
However, manual calibration often proves time-consuming and prone to human error. This is where automated calibration comes in.

How Automated Calibration Works in Print Inspection Systems
Automated calibration in printing inspection systems is a sophisticated process designed to ensure accuracy, consistency and efficiency during printing operations. Through adopting advanced technologies, these calibration systems can self-adjust and maintain optimal performance without human intervention.
1. Baseline Calibration
Automated calibration begins with establishing a reference standard. This step involves:
- Reference Material Analysis: Using calibrated charts, grids, or predefined color profiles, the system sets baseline parameters for alignment, color density, and defect thresholds.
- System Initialization: Sensors, cameras, and processing units are aligned to match these baseline standards, ensuring that every subsequent measurement is consistent.
2. Real-Time Data Collection
During production, 100% inspection systems continuously gather data from the printing process:
- Sensor Inputs: Cameras and sensors capture high-resolution images of the printed material.
- Measurement of Key Metrics: Parameters such as color accuracy, registration alignment, and surface quality are measured against the baseline.
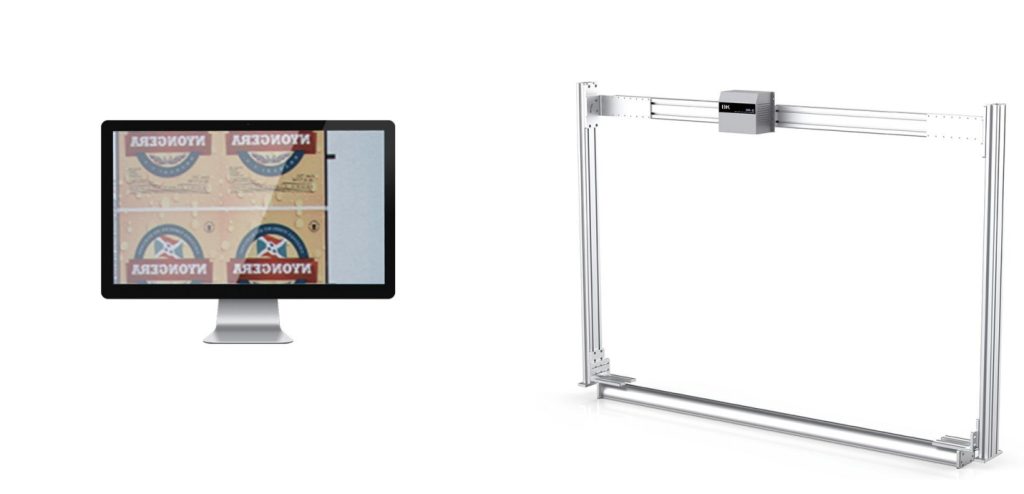
3. Deviation Detection
The collected data is analyzed in real-time to identify any discrepancies:
- Error Identification: Variations in color, smudges, or misalignments are flagged as deviations.
- Threshold Comparison: Deviations are assessed against pre-set tolerances to determine if corrective action is needed.
4. Dynamic Adjustment
When discrepancies are detected, the system initiates automatic corrections:
- Color Correction: Adjusting ink density to match the desired color profile.
- Alignment Adjustment: Recalibrating the positioning of printing components to rectify misalignments.
- Defect Correction: Fine-tuning settings to eliminate recurring defects.
5. Feedback Loop Integration
A critical component of automated calibration is the feedback loop:
- Continuous Monitoring: The system uses feedback to verify the effectiveness of adjustments.
- Self-Learning: Advanced systems incorporate machine learning algorithms to improve calibration accuracy over time by learning from recurring issues.
6. Cloud and Network Integration
Many modern systems are integrated with cloud-based platforms:
- Centralized Updates: Systems receive updates to calibration algorithms, ensuring compatibility with the latest standards.
- Data Sharing: Multiple machines can share calibration data, promoting consistency across production lines.
7. Periodic Recalibration
To maintain long-term reliability, automated calibration systems periodically perform self-checks:
- Scheduled Maintenance: Regular intervals are set for recalibration to account for equipment wear and environmental factors.
- Predictive Adjustments: AI-driven models predict when recalibration is necessary, reducing downtime.

Key Benefits of Automated Calibration in Print Inspection Systems
- Enhanced Accuracy: Automated calibration ensures precise alignment and settings in print inspection systems, reducing human error and enhancing the accuracy of inspections.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating calibration, downtime is minimized, and the system can quickly adapt to new production runs or changes in print specifications.
- Consistent Quality Control: Automated calibration maintains uniform inspection standards across different production batches, ensuring consistent print quality.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Manual calibration processes require skilled labor and significant time. Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, saving costs associated with human resources.
- Improved Throughput: With faster and more reliable calibration, production lines can operate at higher speeds without compromising inspection quality.
- Minimized Material Waste: Accurate calibration prevents issues like misalignments or improper detection thresholds, reducing the number of defective prints and material waste.
- Enhanced Data Collection and Reporting: Automated calibration systems often integrate with advanced analytics, providing detailed reports for quality assurance and traceability.
- Scalability: Automated calibration supports the scalability of operations, allowing the system to handle high-volume production with minimal setup time.

Applications of Automated calibration in Different Printing Industries
- Offset Printing: In offset printing, automated calibration ensures consistent ink density and color reproduction across large print runs. This helps maintain uniformity in color matching and reduces material waste from misprints.
- Flexographic Printing: Automated calibration in flexographic printing systems optimizes anilox roller pressure and ink flow. This ensures consistent print quality on flexible substrates, especially in high-volume packaging production, such as labels and corrugated boxes.
- Gravure Printing: Automated calibration improves the precision of ink metering and consistency in gravure printing. This is particularly valuable in high-end applications like flexible packaging and magazines, where print quality is critical.
- Digital Printing: In digital printing, automated calibration systems adjust color profiles, ink densities, and registration settings in real-time. This leads to accurate, high-quality prints on demand, with faster turnaround times and minimal setup between jobs.
- Screen Printing: Automated calibration helps in screen printing by ensuring proper mesh tension and ink viscosity settings, leading to better image resolution and uniformity. This is especially useful in textile printing, promotional products, and signage.
- Wide-Format Printing: For large-format printing, automated calibration ensures that color consistency, image sharpness, and alignment are maintained across expansive print areas. This is essential for high-quality banners, posters, and vehicle wraps.
- 3D Printing: In 3D printing, automated calibration systems are used to adjust print head position, layer height, and material extrusion rates. These adjustments help achieve high precision in the creation of prototypes, models, or finished products.
- Packaging Printing: Automated calibration is used to ensure that color accuracy and print quality meet industry standards in packaging applications. It plays a crucial role in the production of consistent branding and labeling for consumer goods.
- Newspaper and Commercial Printing: In newspaper and commercial printing, automated calibration reduces setup time and ensures consistent quality for fast-paced, high-volume print runs. This includes ensuring proper alignment, color fidelity, and sharpness.
- Security Printing: For applications like currency, identification cards, and other secure documents, print inspection systems equipped with automated calibration ensures precise registration, color consistency, and the correct application of security features, reducing the risk of errors and fraud.

Challenges and Future Trends of Automated Calibration in Print Inspection System
This chart highlights the current challenges and the trends that will shape the future of automated calibration in print inspection systems.
| Category | Challenges | Future Trends |
| Accuracy and Precision | – Calibration inconsistencies in varying print materials and conditions. | – Development of advanced sensors for more accurate measurements. |
| Integration with Existing Systems | – Difficulty in integrating automated calibration with legacy inspection systems. | – Seamless integration with AI-powered inspection systems for real-time adjustments. |
| Cost of Implementation | – High initial costs for implementing automated calibration systems. | – Decreasing costs due to advancements in technology and economies of scale. |
| Environmental Variations | – Impact of temperature, humidity, and light on calibration accuracy. | – Adaptive calibration systems that adjust to environmental changes automatically. |
| Real-Time Performance | – Time delay in calibration adjustments impacting web inspection system for printing quality. | – Instant, continuous recalibration capabilities with real-time feedback. |
| Data Management | – Overload of calibration data leading to storage and processing challenges. | – Cloud-based solutions for managing large datasets efficiently. |
| User Expertise | – Need for skilled operators to monitor and manage calibration systems. | – More intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and automatic calibration systems. |
| Maintenance and Downtime | – Frequent system downtime and maintenance of complex calibration equipment. | – Predictive maintenance using AI to forecast calibration system issues. |
| Consistency across Production Runs | – Variability in print quality from batch to batch due to calibration drift. | – Machine learning algorithms that continuously monitor and optimize calibration. |

In conclusion, automated calibration in print inspection systems becomes a necessity for modern printing operations. Through ensuring high accuracy, reducing waste, and enhancing productivity, it paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in the printing industry.


