The Pivotal Role of Integrating Web Tension Control and Web Guide Systems in Material Handling
Table of Contents
In industries where precise handling of materials is essential, such as printing, packaging, textiles, and film production, the integration of web tension control and web guide systems is pivotal. These systems ensure the smooth operation of production lines, maintain the quality of the final product, and minimize waste. This article explores the significance, advantages, and technical aspects of integrating web tension control with web guide systems.
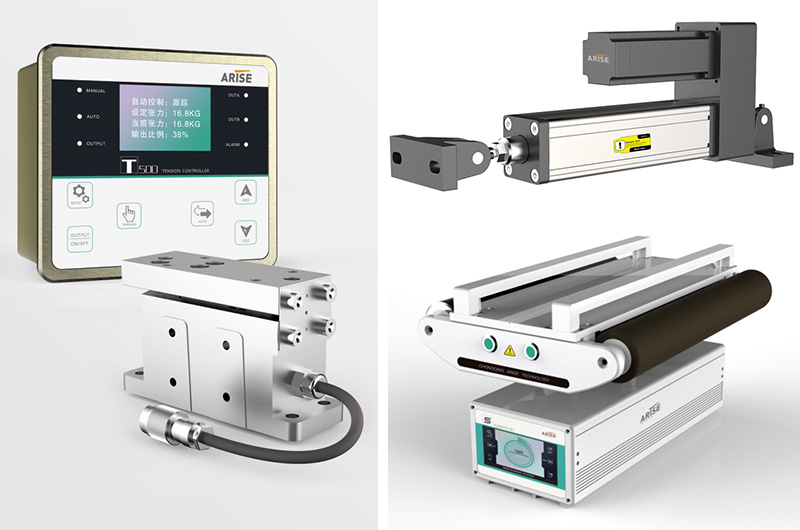

Understanding Web Tension Control and Web Guide Systems
Web Tension Control
Web tension control systems regulate the tension in a continuous strip of material, known as the web, as it moves through the production process. Proper tension ensures the web remains flat and wrinkle-free, preventing defects such as stretching, tearing, or misalignment.
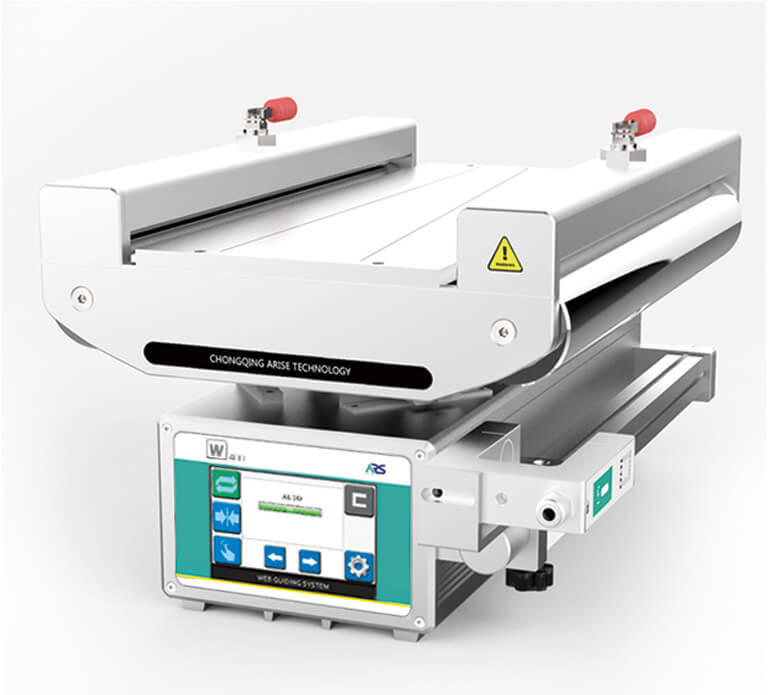
Web Guide System
A web guide system is responsible for maintaining the lateral position of the web as it moves through the production line. This system uses sensors, actuators, and controllers to detect deviations from the desired path and correct them in real-time.

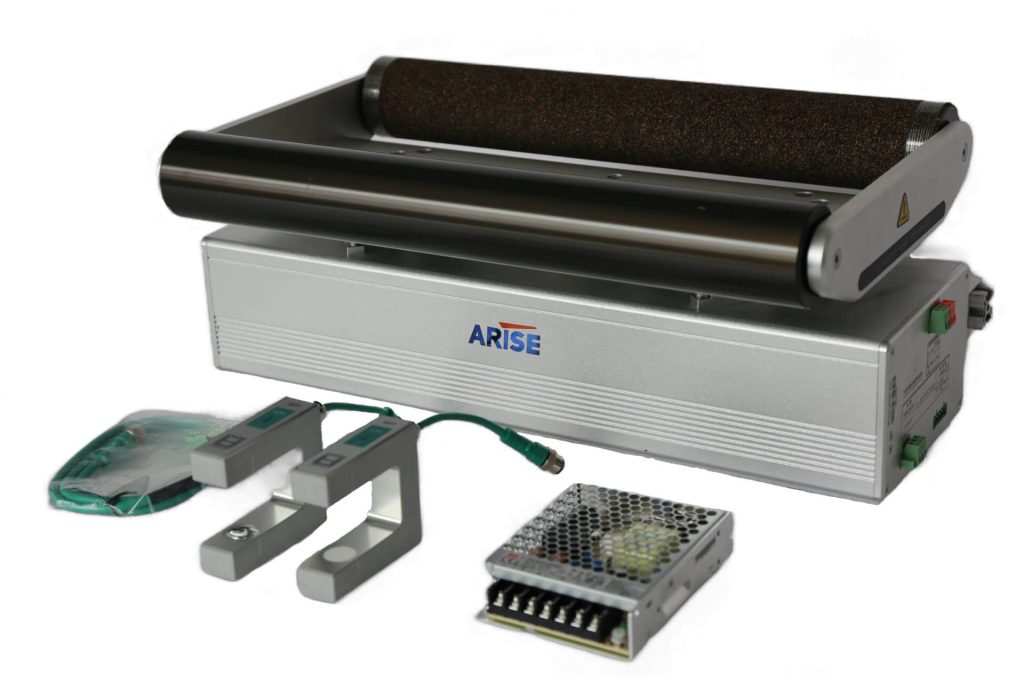
Why Need Integrating Web Tension Control and Web Guide Systems
- Interdependence of Tension and Alignment: Tension influences how the web behaves during guiding; a loosely controlled web may not follow the guide system’s corrections effectively. Similarly, misalignment can result in uneven tension distribution across the web, impacting product quality.
- Precision and Synchronization: Integrated systems ensure that adjustments to tension and alignment occur simultaneously, minimizing the risk of errors.
- Improved Production Speed: In high-speed production lines, rapid corrections are necessary to maintain quality. Integrated systems provide real-time adjustments, enabling faster throughput without compromising standards.
- Material-Specific Handling: Different materials require tailored tension and guiding settings. Integration allows for dynamic adjustments based on material properties, ensuring consistent quality across a variety of applications.

Key Benefits
- Improved Product Quality: Uniform tension and precise alignment minimize defects like wrinkles, misaligned prints, and damaged edges.
- Increased Production Speed: Integrated systems enhance operational speed without compromising quality, meeting the demands of high-volume production.
- Reduced Material Waste: Accurate adjustments prevent material damage, significantly lowering scrap rates and production costs.
- Enhanced Equipment Lifespan: Proper tension and alignment reduce mechanical stress on machinery, leading to fewer breakdowns and extended equipment life.
- Energy Efficiency: Integrated systems optimize energy usage by reducing unnecessary adjustments and ensuring smoother operations.

Key Components of A System Integrating Web Tension Control and Web Guide System
1. Sensors
Sensors form the foundation of the integrated system, providing real-time data on tension levels and web positioning.
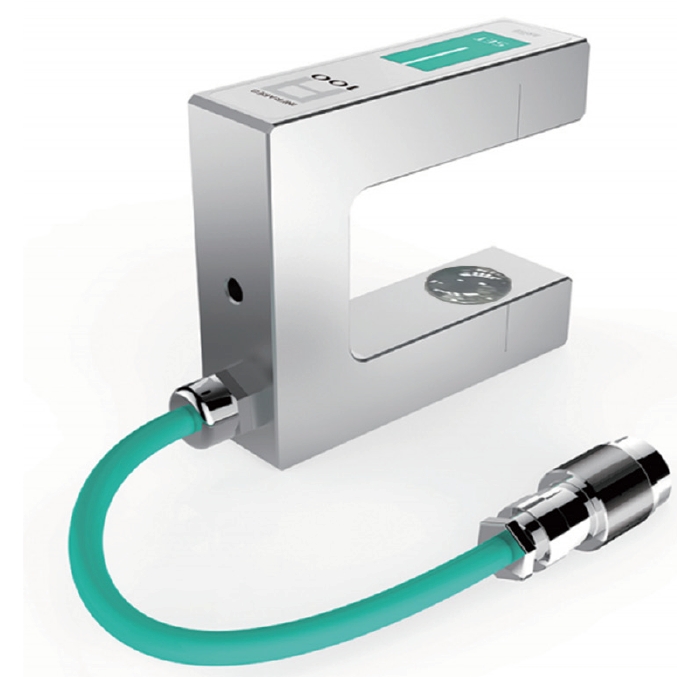
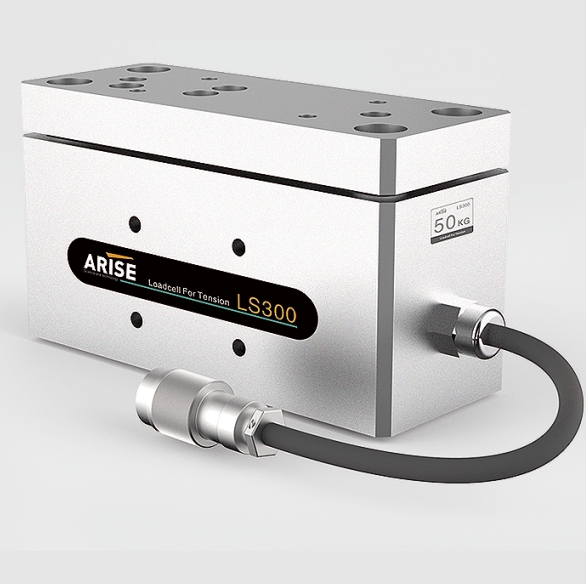
- Load Cells: Measure the force exerted by the web to monitor tension. Load cells detect even minute changes, ensuring accurate tension control. They are commonly used in tension zones like unwinding, rewinding, or mid-process.
- Edge Guide Sensors: Use ultrasonic, infrared, or laser technology to detect the web’s edge position. Essential for lateral alignment in the web guide system.
- Tension Rollers: Embedded with strain gauges, these rollers monitor tension distribution across the web’s width, identifying uneven forces.

2. Controllers
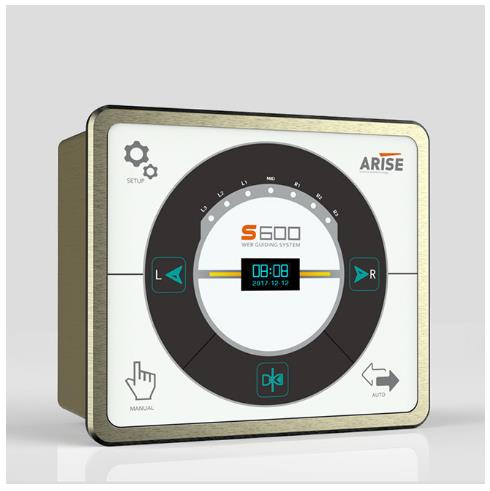
Controllers act as the central processing units, interpreting data from sensors and making adjustments in real time.
- Tension Controllers: Adjust motor speeds or braking systems to maintain consistent tension across the web. They can be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic.
- Web Guide Controllers: Process edge or line sensor data to correct the web’s lateral position by sending signals to actuators. Advanced controllers often include predictive algorithms to anticipate and correct deviations proactively.
- Integrated Controllers: Combine tension and guiding adjustments into a single unit, allowing seamless synchronization between the two functions.

3. Actuators
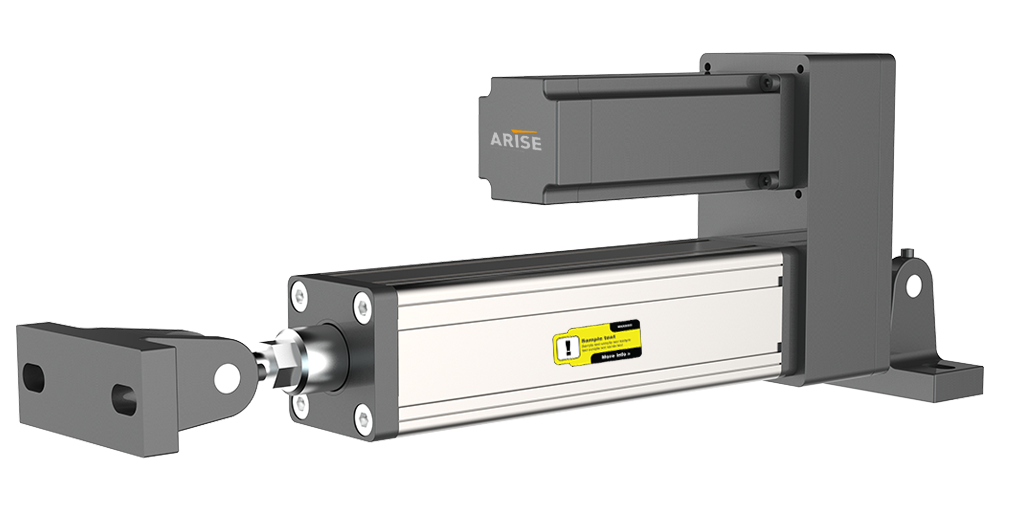
Actuators implement the adjustments calculated by the controllers, ensuring precise corrections.
- Steering Rollers: Adjust the web’s path by changing the angle of the web guiding roller. They are common in systems where the web’s lateral position needs frequent adjustments.
- Electromagnetic Brakes and Clutches: Control web tension by modulating the resistance on the unwind or rewind rollers.
- Servo Motors: Provide precise movement to guide or tension the web, especially in high-speed applications.
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Systems: Used in heavy-duty applications where significant force is required for adjustments.

4. Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback loops ensure real-time monitoring and adjustment of system performance.
- Closed-Loop Feedback: Continuously compares sensor data with set parameters and adjusts tension or alignment accordingly.
- Open-Loop Systems: Operate without real-time adjustments but rely on pre-set parameters for consistent performance.
5. Communication Systems
Efficient communication between components is critical for synchronization.
- Industrial Protocols: Protocols like Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, and Modbus ensure seamless data exchange between sensors, controllers, and actuators.
- Wireless Connectivity: Allows remote monitoring and adjustments, improving flexibility and reducing downtime.
6. User Interface (UI)
The user interface provides operators with control over system settings and performance insights.
- Touchscreen Panels: Allow operators to set parameters, monitor tension and alignment data, and perform manual overrides if necessary.
- Diagnostics and Alerts: Provide detailed performance logs and notify operators of issues like excessive tension, misalignment, or sensor faults.
- IoT Integration: Enables remote access, data logging, and analytics for predictive maintenance and performance optimization.
7. Drive Systems
The drive systems control the speed and torque of the web to ensure consistent movement.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Adjust motor speeds dynamically to maintain uniform tension across the web.
- Precision Rollers: Equipped with high-torque motors for smooth and controlled web transport.
8. Power Supply and Backup Systems
Ensures uninterrupted operation of the integrated system.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Prevents system downtime during power outages.
- Energy-Efficient Designs: Reduce energy consumption, making the system more sustainable.

Industries Benefiting from the Integration of Web Tension Control and Web Guide Systems
This chart summarizes the applications and benefits across various industries, highlighting the importance of integrating web tension control and web guide systems in modern manufacturing.
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
| Printing and Publishing | Offset, gravure, and digital printing | Ensures color registration, prevents misalignment, and minimizes print defects. |
| Packaging | Flexible packaging for food and pharmaceuticals | Maintains design alignment, consistent sealing, and supports high-speed production lines. |
| Textile Manufacturing | Weaving, dyeing, and fabric finishing | Prevents stretching, ensures pattern alignment, and improves coating and lamination efficiency. |
| Film and Foil Production | Plastic films, aluminum foils, and laminates | Prevents distortion, ensures thickness uniformity, and reduces material tearing. |
| Metal Processing | Cutting, coating, and rolling of metal sheets | Ensures positioning during stamping, prevents rolling defects, and enhances surface quality. |
| Paper and Pulp | Paper rolls and sheets for packaging and printing | Prevents tearing, ensures smooth coating, and reduces edge damage and misalignment. |
| Battery and Electronics | Electrode sheets and separator films | Maintains alignment of multi-layer components and reduces defects in electrode assembly. |
| Label and Adhesive Tape | Printing and cutting of labels and tapes | Ensures design accuracy, maintains tension, and minimizes material waste during production. |
| Aerospace and Automotive | Composite materials and laminates | Maintains alignment in lightweight materials and ensures precision in high-value applications. |
| Medical and Pharmaceutical | Medical films and pharmaceutical packaging | Ensures printing accuracy, maintains tension in sterile films, and supports quality control. |

Challenges and Solutions in Integrating Web Tension Control and Web Guide Systems
This chart provides an overview of common challenges faced during the integration of web tension control and web guiding systems, along with practical solutions to address these issues effectively.
| Challenge | Explanation | Solution |
| Sensor Compatibility | Different sensors for tension and alignment may not communicate effectively. | Use standardized sensors and communication protocols like Ethernet/IP or Modbus. |
| System Lag | Delays in adjustments can cause misalignment or uneven tension. | Implement real-time data processing and closed-loop feedback systems. |
| Material Variability | Different materials have varying tension and alignment requirements. | Employ adaptive controllers with pre-programmed material-specific parameters. |
| Mechanical Wear | Components like rollers and actuators may degrade over time, impacting performance. | Schedule regular maintenance and use predictive maintenance tools enabled by IoT. |
| High-Speed Operations | Faster production lines increase the risk of errors in tension and guiding adjustments. | Use high-performance servo motors and advanced algorithms for predictive error correction. |
| Space Constraints | Limited space in production lines can hinder the integration of additional systems. | Design compact, modular systems that combine tension and guiding functionalities. |
| Operator Training | Operators may struggle with the complexity of integrated systems. | Provide intuitive user interfaces and comprehensive training programs. |
| Cost of Integration | Initial investment for integration can be high. | Focus on long-term ROI by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and enhancing product quality. |
| Energy Efficiency | Integrated systems can increase power consumption if not optimized. | Use energy-efficient components and regenerative braking systems. |
| Data Synchronization Issues | Misalignment between data streams from different components. | Implement centralized controllers that synchronize data from all sensors and actuators. |
| Software Compatibility | Legacy systems may not integrate smoothly with modern software. | Upgrade to compatible software platforms and use middleware for seamless integration. |
| Real-Time Monitoring Challenges | Difficulties in tracking and correcting errors in real time. | Deploy advanced sensors with AI-driven analytics for proactive adjustments. |

Conclusion
The integration of web tension control and web guide systems represents a critical advancement in material handling technologies. Through combining the strengths of these systems, industries can achieve superior precision, efficiency, and product quality while reducing waste and operational costs.

