Precision Control in High-speed Web Guide Systems
Table of Contents
In industries where continuous materials such as paper, film, textiles, or metal are processed, maintaining precise alignment is critical to ensuring high-quality output. High-speed web guide systems are engineered to manage this alignment with exceptional accuracy, especially in fast-paced manufacturing environments. These systems are pivotal in sectors like printing, packaging, and textiles, where even the slightest misalignment can lead to significant defects, waste, and inefficiencies.
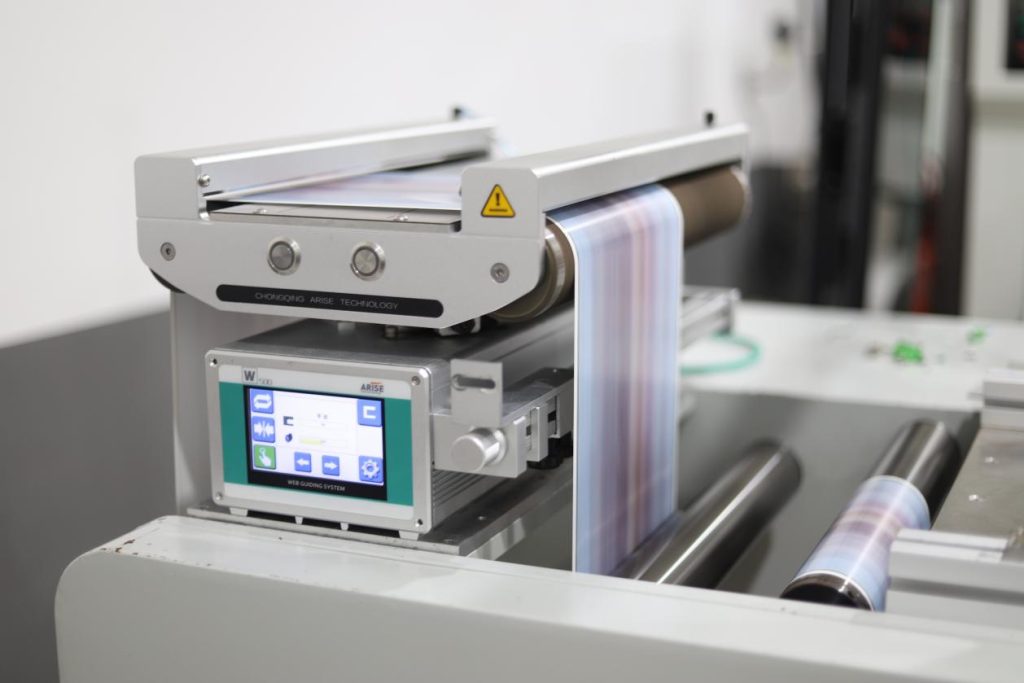

The Critical Role of Precision in Web Guide Systems
Precision in web guide systems ensures that the material, or “web,” is consistently aligned as it moves through various stages of production.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that the material remains properly aligned throughout the production process leads to a higher quality end product. Any deviation can result in defects that compromise the product’s integrity and performance.
- Material Efficiency: Accurate guidance minimizes waste by reducing the likelihood of errors that would necessitate scrapping material. In high-speed operations, even small misalignments can lead to significant material losses.
- Operational Efficiency: High precision allows these systems to operate at faster speeds without sacrificing accuracy. This not only boosts productivity but also reduces downtime and maintenance needs.
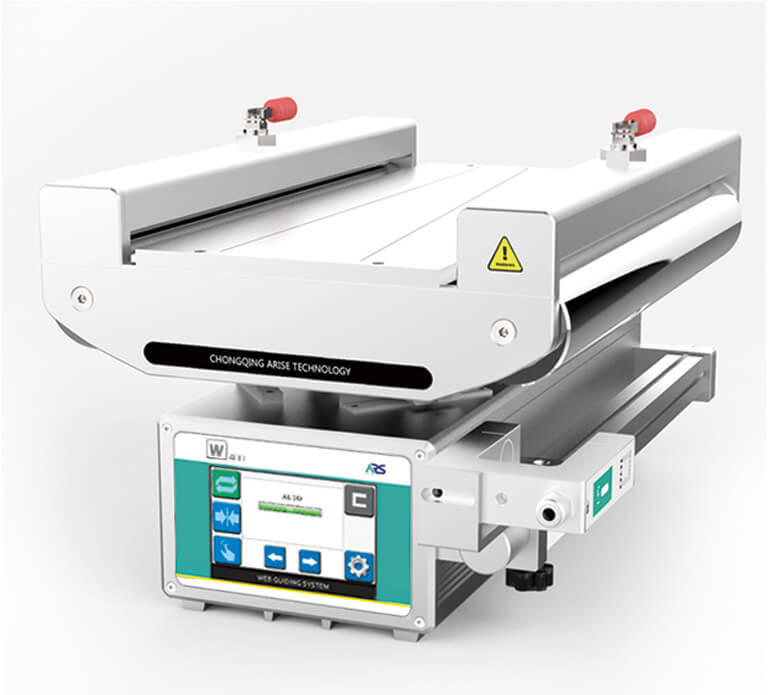

Key Components of Precision Control in Web Guide Systems
The ability to precisely guide web materials directly impacts the quality, efficiency, and consistency of the final product. Several key components work together to achieve this level of control.
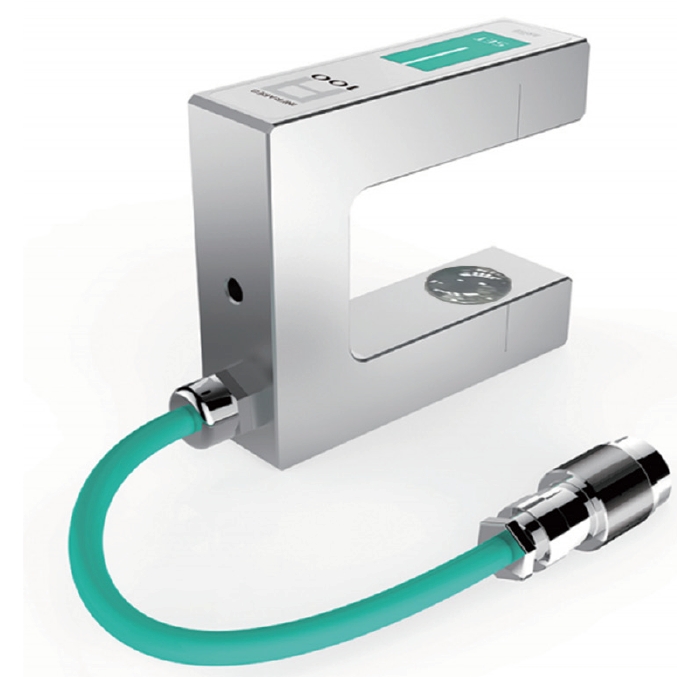
1. Sensors
Sensors are the primary components responsible for detecting the position of the web. They continuously monitor the material’s alignment and provide real-time data to the control system. The choice of sensor depends on the type of material being processed and the specific requirements of the application.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Ideal for detecting the position of opaque or transparent materials, ultrasonic edge sensors use sound waves to measure distance and alignment.
- Optical Sensors: These sensors are highly accurate and are used for materials that have defined edges or markings. They rely on light to detect the position of the web.
- Infrared Sensors: Infrared sensors are useful for detecting the edges of materials that may not be easily visible to other types of sensors.

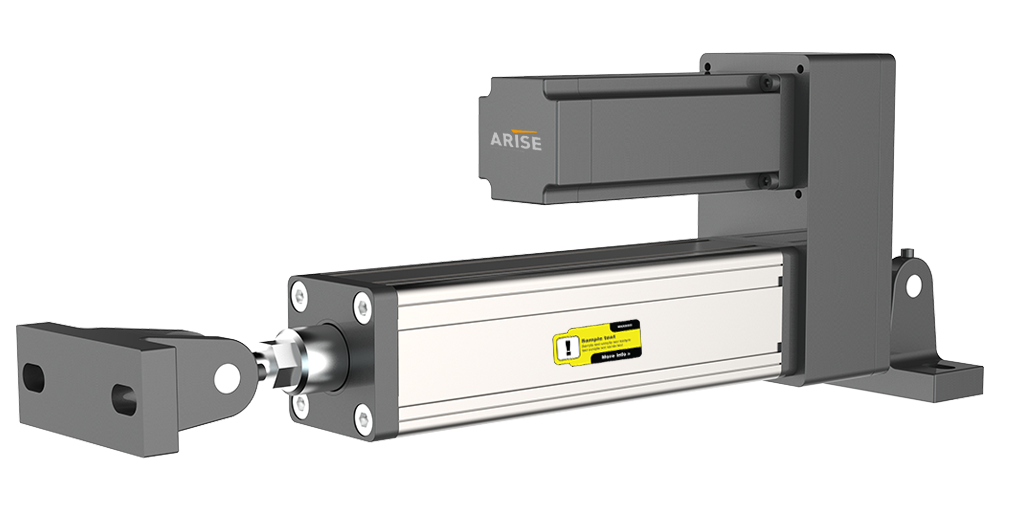
2. Actuators
Web guide actuators are responsible for physically adjusting the position of the web based on the data received from the sensors. They are the “muscle” of the web guide system, making real-time corrections to ensure precise alignment.
- Electromechanical Actuators: These are commonly used in web guide systems for their precision and reliability. They convert electrical signals into mechanical movement to adjust the web’s position.
- Pneumatic Actuators: Often used in systems where rapid movement is required, pneumatic actuators use compressed air to control the web’s position.

3. Control Systems
The control system acts as the “brain” of the web guiding system. It processes the data received from the sensors and sends commands to the actuators to make necessary adjustments. Advanced control algorithms are used to ensure that these adjustments are made quickly and accurately, even at high speeds.
- PID Controllers: Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers are commonly used in web guide systems. They continuously calculate the error between a desired position and the actual position and make adjustments to minimize this error.
- Adaptive Control Systems: These systems can adjust their parameters in real-time based on changing conditions, making them ideal for high-speed operations where precision is critical.

4. Guides
Guides are mechanical components that physically direct the web along its path. They are essential for maintaining the correct alignment and can be adjusted to accommodate different material widths and positions.
- Edge Guides: These track the edges of the material, ensuring that the web remains aligned with the machine’s path. Web edge guide systems are particularly useful for materials with consistent edge characteristics.
- Center Guides: These guides keep the material centered on the path, which is important for processes that require precise centering of the web.
5. Tension Control Systems
Maintaining consistent tension is crucial for precise web alignment. Tension control systems monitor and adjust the tension of the material to prevent slack or excessive pull, which can cause misalignment.
- Load Cells: These devices measure the tension in the web and provide feedback to the control system, which then adjusts the tension accordingly.
- Dancer Rolls: Used to absorb fluctuations in tension, dancer rolls help maintain a steady tension by moving up or down in response to changes in the web’s tension.
6. User Interface
The user interface allows operators to monitor and control the web guide system. Advanced interfaces provide real-time data visualization, system diagnostics, and control adjustments, making it easier to maintain precision control.
- Touchscreen Displays: These provide intuitive control and monitoring, allowing operators to quickly adjust settings and respond to system alerts.
- Remote Monitoring: Some systems offer remote monitoring capabilities, enabling operators to oversee and control the system from a distance.
Challenges in Precision Control for High-speed Web Guide Systems
| Challenges | Description | Impact |
| Sensor Accuracy | Ensuring sensors accurately detect the web’s position at high speeds. | Misalignment, reduced product quality. |
| Response Time | Actuators must respond instantly to sensor feedback to correct deviations. | Delays can lead to significant misalignment. |
| Vibration and Mechanical Noise | High-speed operations often cause vibrations, which can interfere with sensor readings and actuator performance. | Inaccurate adjustments, increased wear. |
| Material Variability | Differences in material properties, such as thickness or elasticity, affect how the web behaves. | Difficulty in maintaining consistent control. |
| Environmental Factors | Temperature, humidity, and dust can impact sensor performance and material behavior. | Inconsistent web alignment, system errors. |
| Tension Fluctuations | Maintaining consistent tension is challenging, especially at high speeds. | Slack or excessive tension can cause defects. |
| System Integration | Integrating web guide systems with other machinery while maintaining precision. | Potential for synchronization issues. |
| Maintenance and Calibration | Regular maintenance is required to ensure the web guiding system remains precise. | Downtime, reduced precision over time. |
| Data Processing Speed | The control system must process sensor data and issue commands in real-time. | Lag can result in errors in web alignment. |
| Operator Training | Operators must be trained to manage and troubleshoot precision control systems effectively. | Errors due to improper adjustments. |

Innovations in Precision Control for High-speed Web Guide Systems
As production speeds increase, so does the demand for innovations that enhance the precision, reliability, and efficiency of web guide control systems, addressing common challenges and shaping the future of precision control in high-speed web guide systems.
1. Advanced Optical and Laser Sensors
The integration of advanced optical and laser sensors has dramatically improved the accuracy of web guide systems. These sensors provide high-resolution, real-time feedback on the position of the web, enabling the system to make rapid adjustments. Laser sensors, in particular, offer precise detection capabilities even at high speeds, reducing the likelihood of material drift and ensuring consistent alignment.
2. AI-powered Control Algorithms
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in the precision control of web guide systems. AI-powered algorithms analyze vast amounts of data in real time, predicting potential alignment issues before they occur. By learning from past adjustments and continuously optimizing control parameters, these algorithms reduce manual intervention and enhance the overall stability of the system.
3. High-speed Actuation Systems
Innovations in actuator technology have led to the development of faster and more responsive actuators. These high-speed actuation systems are capable of making minute adjustments in fractions of a second, ensuring that the web remains perfectly aligned even under rapidly changing conditions. The result is a significant reduction in errors and material waste.
4. Real-time Data Analytics and Monitoring
The ability to monitor and analyze data in real time has greatly enhanced the precision of web guide systems. Advanced data analytics tools process information from sensors and other inputs, providing operators with immediate insights into system performance. This real-time feedback allows for quick adjustments, preventing misalignments and ensuring continuous operation at optimal speeds.

5. IoT Integration for Enhanced Connectivity
The Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled unprecedented levels of connectivity in web guide systems. IoT-enabled devices and sensors communicate seamlessly with central control systems, creating a cohesive network that ensures all components are synchronized. This integration not only improves precision but also facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing overall system efficiency.
6. Adaptive Control Systems
Adaptive control systems represent a significant leap forward in precision control technology. These systems dynamically adjust their behavior based on real-time conditions, such as changes in material tension or speed. By continuously adapting to the operating environment, these systems maintain optimal performance, even in challenging scenarios, ensuring consistent material alignment at high speeds.
7. Enhanced User Interfaces with Predictive Capabilities
Modern web guide system equipment feature enhanced user interfaces that offer operators detailed visualizations of system status and performance. These interfaces often include predictive capabilities, alerting operators to potential issues before they impact production. By providing intuitive control and monitoring options, these interfaces make it easier to maintain precision in high-speed environments.

8. Energy-efficient Technologies
Energy efficiency is becoming increasingly important in the design of high-speed web guide systems. Innovations in motor design, material selection, and control algorithms have led to systems that consume less energy while maintaining high levels of performance. These energy-efficient technologies not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to a more sustainable production process.
9. Modular System Designs
Modularity is a key innovation that allows web guide systems to be easily adapted to different production needs. Modular designs enable quick upgrades or replacements of specific components without requiring a complete system overhaul. This flexibility is particularly valuable in high-speed environments, where minimizing downtime is crucial.
Overall, As manufacturing demands continue to advance, the role of web guide systems in ensuring consistent, high-quality output at high speeds will become increasingly vital. With ongoing advancements in technology, high-speed web guiding systems are poised to deliver even greater levels of precision and efficiency, driving innovation and excellence in production processes.

