How Web Guide Systems are Used for Handling Non-standard Materials
Table of Contents
Web guide systems are essential in industries where materials are processed in continuous forms, such as soils, paper, plastic films, etc. Their primary function is to control the alignment of these materials during production to prevent misalignment, wrinkles, and other issues. While web guide systems have been optimized for standard materials, they must be adapted for non-standard materials, which present unique challenges due to their specific properties.
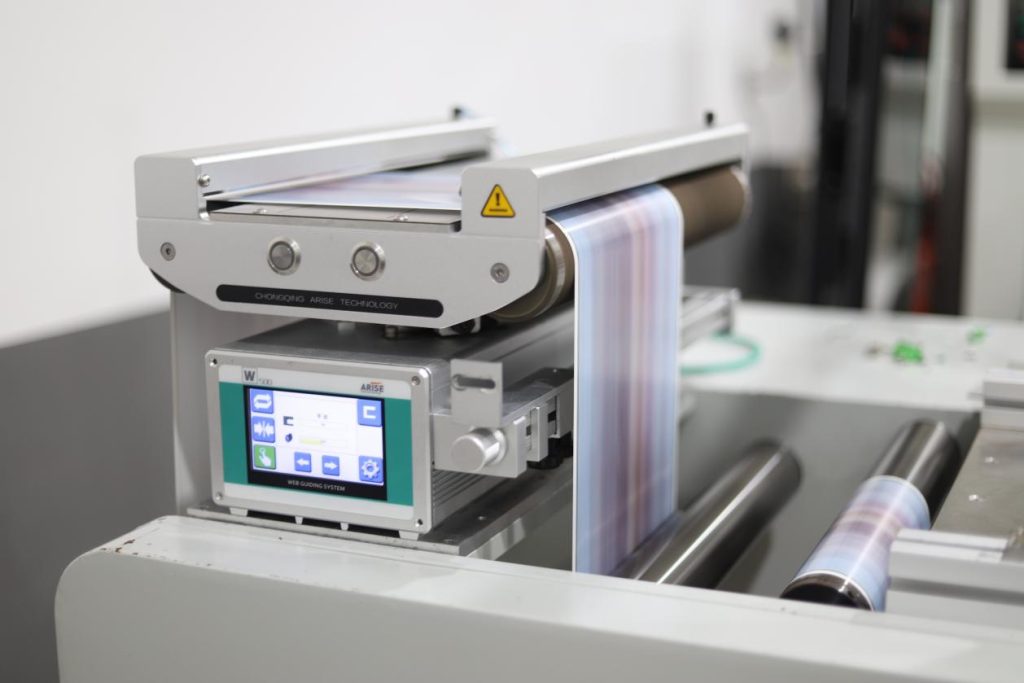

Understanding Non-standard Materials
Non-standard materials refer to any materials that deviate from conventional specifications in terms of width, thickness, or flexibility. Examples include:
- Specialized films and foils: Thin, high-stretch films or multilayered foils used in packaging or electronics.
- Textiles: Fabrics that are either too lightweight, highly elastic, or have irregular surfaces.
- Advanced composites: Materials used in aerospace and automotive industries that are both lightweight and strong but may behave unpredictably.
- Metal strips: Particularly thin or unusually coated metal strips used in applications like flexible electronics.
These materials often have challenging characteristics that require customized handling to maintain alignment throughout the manufacturing process.
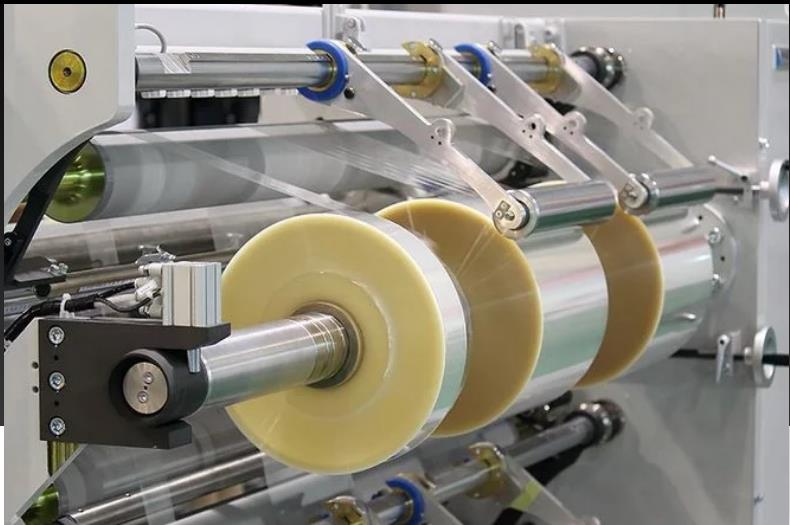

Challenges in Guiding Non-standard Materials
This chart highlights the key challenges in guiding non-standard materials, their descriptions, and the potential impacts they can have on the production process.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
| Thickness and Surface Variability | Inconsistent material thickness or uneven surface finishes. | Uneven tension distribution, misalignment, wrinkles, and potential material damage. |
| Elasticity and Stretchability | Materials that stretch or have varying elasticity. | Material deformation, misalignment, slippage, or tears due to tension fluctuations. |
| Slippery or Sticky Surfaces | Materials with slippery or sticky coatings. | Slippage, jamming, or material buildup that disrupts alignment and processing efficiency. |
| Friction Coefficients and Material Interaction | Unpredictable friction between material and web guide system components. | Slippage, misalignment, excessive wear, or difficulty in controlling material movement. |
| Delicate or Irregular Edges | Materials with delicate or uneven edges. | Increased risk of misalignment, material wander, wrinkles, folds, or damage. |
| Sensitivity to Tension and Handling | Sensitive materials prone to damage under improper tension. | Breakage, tears, or deformation from excessive tension or poor handling during processing. |

Key Features of Web Guide Systems for Non-standard Materials
1. Adaptive Rollers and Dynamic Tension Control
- Functionality: Adaptive rollers can automatically adjust their position to accommodate variations in material thickness, stretchability, or surface conditions. This dynamic adjustment ensures consistent alignment even as the material changes during processing.
- Benefit: This feature is crucial for non-standard materials that may vary in tension or elasticity, as it helps prevent material deformation or misalignment while maintaining optimal processing conditions.
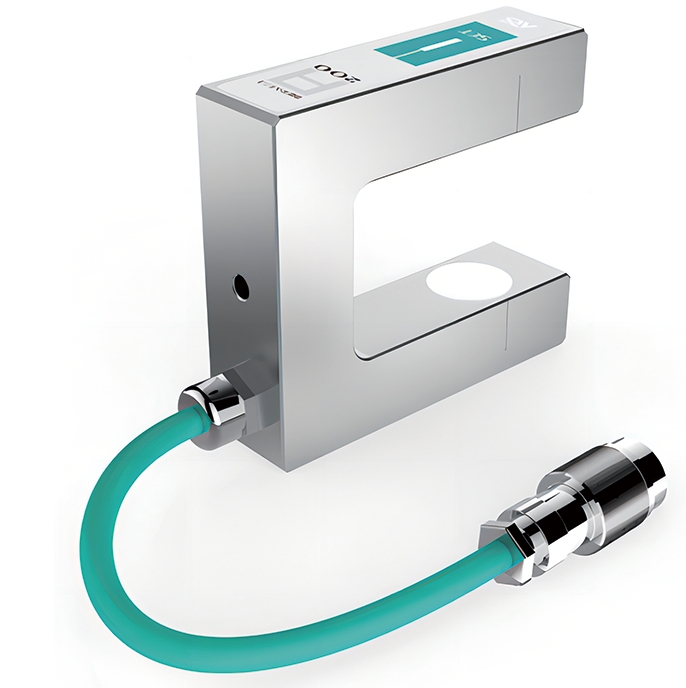
2. Precision Sensors
- Functionality: Advanced edge sensors, optical sensors, and laser-based measurement devices are used to detect slight misalignments or shifts in the material. These sensors are highly sensitive and can detect discrepancies that might not be visible to the naked eye.
- Benefit: For non-standard materials like thin films or textiles with varying surface finishes, precision web guide sensors ensure that even the smallest misalignment is corrected in real-time, maintaining production quality.

3. Variable Speed Servo Motors
- Functionality: Servo motors allow for the precise adjustment of rollers or guiding components based on the material’s speed, stretch, and tension. These motors can vary speed dynamically to match the material’s behavior during processing.
- Benefit: Non-standard materials, such as elastic fabrics or stretch films, require the web guide system to adapt to varying speeds and forces. Variable speed motors help prevent material damage caused by sudden changes in tension or speed.
4. Advanced Tension Control Mechanisms
- Functionality: Web guiding control systems for non-standard materials often feature advanced tension control systems, such as pneumatic or electronic tensioners, that respond to real-time data about the material’s behavior. These systems adjust the amount of tension applied to the material to maintain stability and prevent issues like sagging or stretching.
- Benefit: Non-standard materials with irregular elasticity or thickness can benefit from consistent and adjustable tension, reducing the risk of defects and ensuring smooth handling.

5. Specialized Roller Coatings and Materials
- Functionality: Rollers used in web guiding systems for non-standard materials are often coated with specialized materials such as rubber, ceramic, or non-marking coatings to prevent surface damage. These coatings help protect delicate films, foils, and textiles from scratching, scuffing, or abrasion.
- Benefit: Delicate or sensitive materials like plastic films and metallic foils need to be guided without damaging their surface finish. Special roller coatings minimize friction while preventing harm to these materials.
6. Intelligent Control Systems
- Functionality: Web guiding systems for non-standard materials often include intelligent digital web guide controller that monitor and adjust system parameters in real time. These systems use data from sensors to optimize the guiding process and improve accuracy over time.
- Benefit: Adaptive algorithms in intelligent control systems help the web guide to “learn” the behavior of specific materials, adjusting settings automatically for optimal alignment, even as material properties change during the production run.
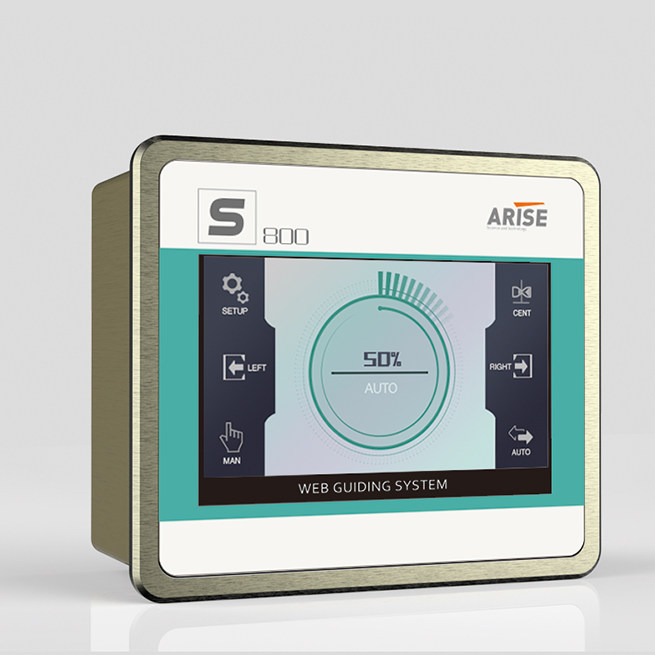

7. Customized Guide and Edge Detection Systems
Functionality: Non-standard materials often require customized web guide systems. For example, materials with irregular edges or complex shapes might need specialized edge detection systems, including ultrasonic or optical sensors, that can detect the edges of the material no matter how irregular or flexible.
Benefit: This customization ensures that the material remains aligned throughout the process, preventing edge wander or misalignment, which is especially common in flexible or complex materials.

8. Real-time Feedback and Monitoring
- Functionality: Advanced web guiding systems offer real-time feedback via integrated displays or machine interfaces, allowing operators to monitor system performance and material behavior continuously.
- Benefit: Continuous monitoring allows for quick intervention if a misalignment or material fault is detected. This feature ensures that non-standard materials are processed efficiently and reduces downtime due to misalignment.

9. Integration with Other Production Systems
- Functionality: Many web guide systems can integrate with other equipment such as unwinders, slitters, or winders, enabling a seamless production flow. This integration allows for synchronized control of the material path from one machine to the next.
- Benefit: For complex materials or high-speed production, the integration of web guide systems with other machines ensures that the entire production line functions smoothly without material interruptions.
10. Flexible Mounting and Adjustment Options
- Functionality: Web guiding systems designed for non-standard materials often feature flexible mounting options and easy adjustability. These systems can be repositioned or reconfigured based on the material and the production setup.
- Benefit: Non-standard materials often require frequent changes in processing conditions. Flexible mounting and adjustable systems ensure that the web guide can accommodate various material types and production needs without extensive downtime or reconfiguration.
Applications of Web Guide Systems for Non-standard Materials
This chart highlights various industries, materials, applications, and the benefits of using web guide systems for non-standard materials.
| Industry | Material Type | Application | Advantages |
| Packaging Industry | Flexible films, laminates, multi-layer packaging | Ensuring proper alignment during printing, coating, and lamination processes | Prevents misalignment, wrinkles, and material damage during high-speed processing. |
| Textile Industry | Fabrics, woven materials, textiles | Handling materials with irregular edges and stretch characteristics during processing | Prevents distortion, wrinkles, and ensures precise alignment of fabrics during processing. |
| Electronics Industry | Flexible printed circuits (FPC) | Managing delicate, thin, and flexible circuits during assembly, printing, and testing | Maintains alignment, preventing component misplacement or damage to circuits. |
| Metal Industry | Thin metal foils and strips | Managing foils and strips during slitting, coating, or heat treatment | Reduces risk of misalignment and material damage, ensuring precise slitting and processing. |
| Printing Industry | Specialty paper, films, textured substrates | Ensuring accurate alignment in printing, coating, or laminating processes | Prevents jams, misfeeds, and print defects by keeping material aligned and smooth. |
| Medical Industry | Medical films, sensitive coatings | Handling films with coatings during packaging and production of medical products | Preserves material integrity and prevents contamination or defects during processing. |
| Food Industry | Coated/laminated food wrappers | Managing biodegradable wraps or multi-layer food packaging films during printing and sealing | Maintains packaging integrity and freshness by preventing misalignment and material damage. |
| Automotive Industry | Non-metallic composites and specialized films | Handling insulation materials, component wrapping, or coating films during processing | Prevents misalignment or damage to lightweight and flexible composites, optimizing production efficiency. |
| Aerospace Industry | Composite materials, laminates | Managing composites and laminates during cutting, laying-up, or curing in aerospace applications | Ensures precise alignment, preventing material misalignment or stretching that could compromise structural integrity. |

Conclusion
As industries develop towards more customized and specialized materials, the role of web guiding systems becomes even more critical. Non-standard materials demand higher precision and adaptability from web guiding technologies and advances in sensor technology, motor systems, and roller coatings have enabled manufacturers to address these challenges. Web guide systems for non-standard materials offer the necessary solutions to ensure consistent quality, high productivity and reduced waste in various manufacturing industries.

