How to Implement Effective Tension Control for Variable Web Widths
Tension control is a critical factor in web handling processes, especially when dealing with variable web widths. Variations in web width can introduce complexities that affect product quality, process stability, and material efficiency. Implementing effective tension control strategies is essential to maintaining uniformity and preventing defects such as wrinkles, stretching, or web breaks.

Table of Contents
Challenges of Tension Control in Variable Web Widths
| Challenge | Impact | Possible Cause |
| Uneven Tension Distribution | This leads to wrinkles, stretching, or tearing of the web | Inconsistent force application across different widths |
| Material Deformation | Causes elongation, curling, or breakage | Incorrect tension settings for varying material properties |
| Varying Roll Inertia | Results in unstable tension control during speed changes | Changes in mass and rotational dynamics with different widths |
| Sensor Calibration Issues | Reduces accuracy of tension measurement | Difficulty in detecting real-time width variations |
| Delayed Response Time | Causes tension fluctuations and quality defects | Mechanical adjustments may not react quickly to width changes |
| Edge Alignment Problems | Leads to misalignment and uneven stress distribution | Web tracking systems struggle to adjust dynamically |
| Automation Challenges | Increases manual intervention and reduces efficiency | Standard systems lack adaptability for dynamic width changes |
| Component Wear and Tear | Increases maintenance costs and downtime | Frequent tension fluctuations put stress on mechanical parts |
Addressing these challenges requires advanced tension control technologies, such as zonal tension control, real-time sensor feedback and precision servo motor systems, to maintain optimal tension across variable web widths.

Effective Tension Control Strategies for Variable Web Widths
- Zonal Tension Control
In systems where web width fluctuates, implementing zonal tension control is an effective strategy. This involves dividing the web into distinct zones, each with its own tension control system. These zones can be independently adjusted to maintain consistent tension across the varying widths. By controlling tension in specific areas, manufacturers can ensure that any fluctuations in web width don’t affect the overall process, thus preventing defects and improving product consistency.
- Servo-Driven Tension Control
Servo motors offer precise and real-time adjustments in torque and speed, making them ideal for handling variable web widths. Unlike traditional mechanical systems, servo-driven tension control systems can rapidly respond to changes in web width, adjusting the tension instantly to maintain optimal force distribution. This is especially useful in fast-paced environments, such as printing and laminating, where quick adjustments are required to keep the process stable.
- Real-Time Feedback Systems
Integrating advanced sensor technologies like load cells, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared detectors enables real-time monitoring of tension, web position, and width variations. These tension sensors provide continuous feedback to the control system, which can make instant adjustments based on the data collected. By continuously monitoring these parameters, the system can ensure that tension remains uniform across the entire web, regardless of changes in width, improving the final product quality and reducing waste.

- Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology allows manufacturers to create virtual models of their web handling systems, simulating different web widths and tension control settings. This predictive modeling enables engineers to optimize tension parameters before applying them in a real-world setting. By testing various scenarios digitally, manufacturers can fine-tune their control systems, minimizing trial-and-error adjustments and reducing downtime during production.
- Automated Web Width Detection and Adjustment
Automated web width detection systems, typically using optical or ultrasonic sensors, can continuously measure the web’s width in real time. This data is then used to automatically adjust the tension control system to accommodate width variations. By eliminating the need for manual adjustments, these automated systems not only reduce the risk of human error but also improve production efficiency by ensuring consistent tension during each cycle.
- Regular Calibration of Sensors and Systems
For tension control systems to remain effective, regular calibration of sensors and control units is essential. Over time, sensors may drift, and machine settings may need fine-tuning to maintain precise tension control. Routine calibration ensures that systems continue to deliver accurate measurements and adjustments, preventing tension inaccuracies that could lead to product defects and wasted materials.
- Closed-Loop Control Systems
Closed-loop feedback control systems are designed to automatically adjust tension based on real-time measurements, ensuring that the web’s tension remains stable despite any changes in its width. These systems continuously compare the desired tension levels to actual tension data and make necessary adjustments, providing a stable, controlled environment for web handling processes. This eliminates the need for manual intervention and keeps the process efficient.
- Material-Specific Tension Optimization
Different materials require different tension settings. For example, a thicker or more rigid material may require higher tension to maintain uniformity, while a thinner or stretchable material may need less force. By tailoring tension parameters to the specific material being processed, manufacturers can avoid issues like material distortion and ensure higher product quality. This is particularly important in industries such as printing and packaging, where materials vary significantly in both thickness and elasticity.
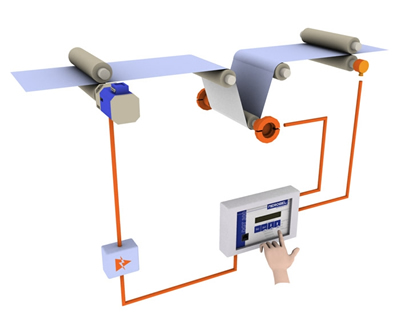
Technological Innovations in Tension Control for Variable Web Widths
1. AI and Machine Learning-Based Control Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming tension control systems by providing more intelligent and adaptive solutions. These systems use historical data, real-time sensors, and predictive algorithms to learn how to adjust tension settings autonomously as web widths change. AI and ML algorithms can optimize tension control by predicting the best settings for different materials and web widths, adapting to changing conditions with minimal human intervention.
2. Automated Edge Alignment Systems
Advanced edge alignment technologies ensure that the web remains properly aligned as it passes through the tension control system. Automated web edge guides, coupled with real-time sensors, track the edges of the web and make adjustments to keep it centered. Proper alignment helps prevent tension imbalances caused by misalignment, which can lead to defects such as uneven tension distribution, wrinkles, or web breaks.

3. Adaptive Tension Control Using Machine Vision
Machine vision systems are being integrated with tension control to further improve the precision of web handling. By using cameras and image processing software, these web inspection vision systems can visually detect changes in web width, detect defects, and measure the distance between web edges. With this visual input, tension control systems can adapt in real-time to the detected changes, ensuring that the web is processed without defects, even as the width fluctuates.

4. Hybrid Tension Control Systems
Hybrid systems combine traditional mechanical tension control methods with digital technologies to offer greater flexibility and precision. For example, a hybrid system may use a mechanical dancer arm in conjunction with an electronic tension sensor. This combination allows for better adaptation to varying web widths, improving accuracy and reducing the complexity of mechanical systems while maintaining the reliability of traditional approaches.
5. Multi-Zone Tension Control
In multi-zone tension control, the web is divided into different sections, each with its own independent tension control system. This approach allows each section of the web to adjust its tension based on local conditions, such as variations in width or material thickness. Multi-zone control ensures that tension is applied evenly across the entire web, preventing defects and ensuring a higher-quality end product.
Key Steps for Optimized Tension Control in Variable Web Widths
These key steps help ensure that tension control systems remain flexible, accurate, and responsive, ensuring higher production quality and operational efficiency in environments with varying web widths.
| Step | Description | Benefit |
| 1. Implement Zonal Tension Control | Divide the web into multiple independent tension zones. | Ensures tension is evenly distributed, compensating for width variations. |
| 2. Integrate Real-Time Web Width Detection | Use optical or ultrasonic sensors to continuously monitor web width. | Enables automatic adjustment of tension in response to web width changes. |
| 3. Use Servo Motors for Precision | Deploy servo-driven motors to control tension with high accuracy and responsiveness. | Allows for fast and precise tension adjustments, ensuring consistent web handling. |
| 4. Incorporate Closed-Loop Feedback | Implement closed-loop systems that adjust tension based on real-time feedback. | Maintains consistent tension across varying web widths and material types. |
| 5. Apply Digital Twin Modeling | Use virtual simulations to predict and optimize tension control strategies. | Reduces risk of errors by testing adjustments in a simulated environment before real-world application. |
| 6. Maintain Automated Edge Alignment | Integrate automated tracking and edge guide systems for precise alignment. | Prevents misalignment, ensuring smooth material flow and consistent tension. |
| 7. Regular Calibration of Sensors | Calibrate sensors and tension systems periodically for accuracy. | Ensures that the system continues to operate with precision over time. |
| 8. Optimize for Material-Specific Tension Settings | Adjust tension settings according to material characteristics (e.g., elasticity, thickness). | Customizes tension control for optimal handling of different materials, reducing defects. |
| 9. Leverage Machine Vision Systems | Integrate machine vision to detect web width and defects, adjusting tension accordingly. | Enhances real-time adjustment of tension and improves product quality by detecting problems early. |
| 10. Monitor and Analyze Data in Real-Time | Continuously analyze performance data from sensors for adjustments. | Provides actionable insights for quick and informed decision-making, improving efficiency and reducing waste. |

Summary
Tension control for variable web widths requires a combination of advanced technology, adaptive strategies, and best practices to ensure process stability and product quality. With the integration of advanced technologies such as AI-driven control, servo-based mechanisms, and zonal tension regulation, manufacturers can achieve superior web handling performance, minimizing defects and optimizing productivity.


