How to Do A Good Job in Printed Packaging Inspection
A well-designed package can convey quality, trust, and brand identity, influencing purchasing decisions and customer loyalty. However, even the most beautifully designed packaging can be undermined by defects or inconsistencies. This is where printed packaging inspection comes into play. This process is crucial for maintaining high standards, ensuring regulatory compliance, and safeguarding brand reputation.

The Importance of Printed Packaging Inspection
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that printed packaging meets the required standards is vital for maintaining the overall quality of the product. Any errors in printing, such as color variations, smudges, or misaligned text and images, can affect the perceived quality of the product and, by extension, the brand.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, especially those dealing with food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, are subject to stringent regulations regarding packaging. Printed packaging must contain specific information, such as ingredients, usage instructions, and safety warnings, all of which must be legible and accurate.
- Brand Integrity: Consistency in packaging is crucial for brand identity. Any deviation in color, font, or design can dilute brand recognition and trust. Regular inspection helps in maintaining uniformity across all printed materials.
- Cost Efficiency: Detecting and correcting errors early in the production process can save significant costs. Packaging defects discovered post-production can lead to waste, recalls, and additional expenses.
Key Aspects of Printed Packaging Inspection
Printed packaging inspection involves several critical elements to ensure the quality, consistency, and compliance of packaging materials.
| Aspect | Description | Purpose | Tools |
| Visual Inspection | Manual or automated check for visible defects. | Detects smudges, misprints, incorrect colors, and other visible flaws. | High-resolution cameras, image processing software. |
| Dimensional Inspection | Verification of correct positioning and size of printed elements. | Ensures proper alignment and size of text, logos, and graphics. | Precision measurement tools, automated systems. |
| Color Verification | Ensuring color consistency and accuracy. | Maintains brand color standards across all packaging batches. | Spectrophotometers, colorimeters. |
| Barcode and QR Code Verification | Checking readability and accuracy of barcodes and QR codes. | Ensures correct functioning for product tracking, inventory management, and consumer use. | Barcode scanners, verification software. |
| Text Verification | Ensuring all printed text is accurate and legible. | Verifies presence and correctness of all required information, especially legal and safety details. | Optical character recognition (OCR) technology. |
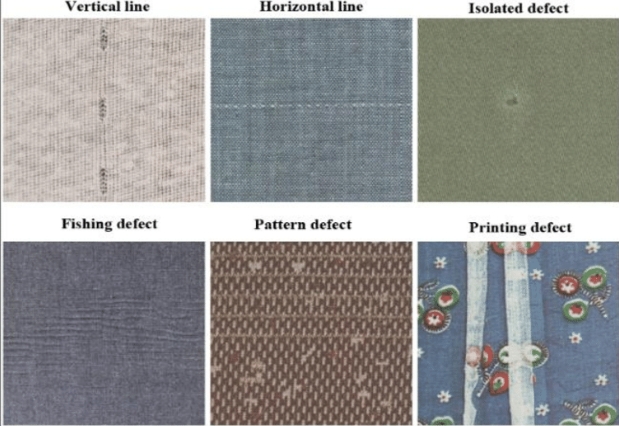
Technologies Used in Printed Packaging Inspection
1. Machine Vision Systems
- Description: Visual printing inspection machine utilizes cameras and image processing software to inspect printed packaging.
- Benefits: Detects defects such as misprints, color variations, and alignment issues with high precision.
- Applications: Used for visual inspection in real-time on production lines.
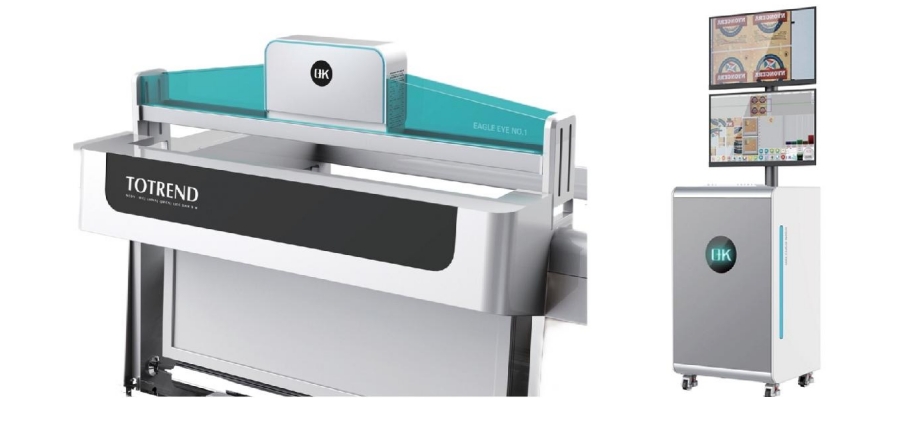

2. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- Description: Offers high-speed inspection capabilities using automated systems.
- Benefits: Ideal for inspecting printed elements for defects, ensuring high throughput and accuracy.
- Applications: Commonly used in electronics and packaging industries.
3. Spectrophotometers and Colorimeters
- Description: Instruments used to measure color accuracy and consistency.
- Benefits: Ensures that printed colors match specified standards across production batches.
- Applications: Critical for maintaining brand consistency and meeting customer expectations.
4. Barcode and QR Code Scanners
- Description: Devices that read and verify barcodes and QR codes printed on packaging.
- Benefits: Ensures accurate scanning and readability throughout the supply chain.
- Applications: Essential for product tracking, inventory management, and consumer engagement.
5. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Technology
- Description: Software technology that recognizes and interprets printed text.
- Benefits: Verifies the accuracy and legibility of text on packaging, including legal and safety information.
- Applications: Used for reading and validating printed text across various packaging formats.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
- Description: Algorithms that enhance inspection capabilities through pattern recognition and data analysis.
- Benefits: Improves defect detection accuracy, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
- Applications: Used for advanced analytics, anomaly detection, and continuous improvement in inspection processes.
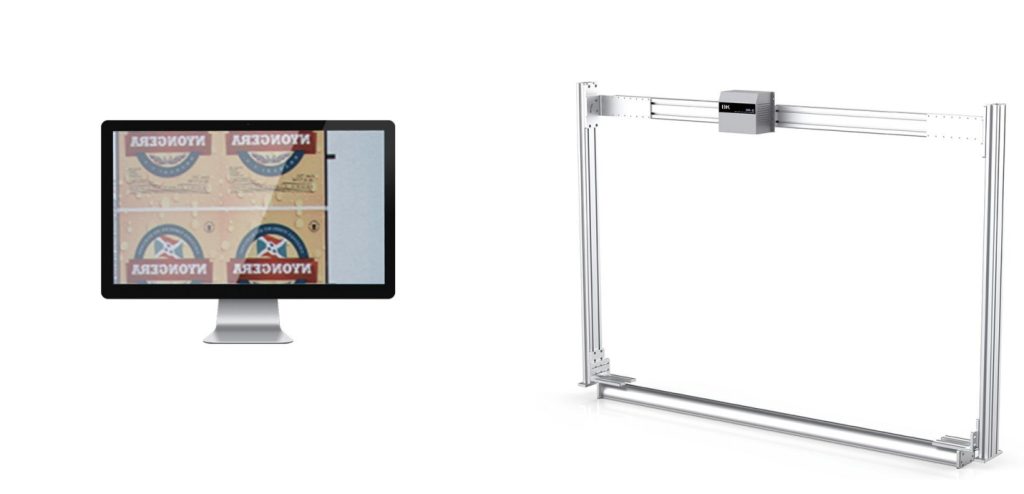

Challenges and Future Directions in Printed Packaging Inspection
Challenges
1. Integration with Production Lines
- Challenge: Seamless integration of inspection systems without disrupting production flow.
- Impact: Misalignment can lead to delays and inefficiencies in production.
2. Adaptability to Diverse Packaging Types
- Challenge: Handling various packaging materials and designs effectively.
- Impact: Inability to adapt may compromise inspection accuracy and thoroughness.
3. Real-Time Data Handling
- Challenge: Managing and processing large volumes of real-time inspection data.
- Impact: Delays in data analysis can hinder timely decision-making and corrective actions.
4. Complexity of Defect Detection
- Challenge: Detecting subtle defects that are not easily visible.
- Impact: Missed defects can affect product quality and consumer perception.
5. Cost of Implementation and Maintenance
- Challenge: High initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of advanced inspection technologies.
- Impact: Affordability may limit adoption, especially for smaller manufacturers.
Future Directions
1. Automation and Robotics
- Direction: Increased use of automation for faster and more precise inspections.
- Impact: Reduced human error, improved throughput, and scalability.
2. IoT and Connectivity
- Direction: Utilizing IoT for interconnected inspection systems and real-time monitoring.
- Impact: Enhanced data collection, analysis, and remote diagnostics.
3. Advanced Analytics and Visualization
- Direction: Development of advanced analytics tools for better data interpretation.
- Impact: Insights into production trends, quality metrics, and process optimization.
4. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions
- Direction: Integration of sustainability practices into inspection processes.
- Impact: Compliance with environmental regulations and reduction of carbon footprint.
5. User Interface and Training
- Direction: Improvements in user interfaces and comprehensive training programs.
- Impact: Enhanced usability, efficiency, and operator proficiency.

Conclusion
Printed packaging inspection is an indispensable part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of quality and consistency. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of inspection systems will only improve, helping manufacturers maintain brand integrity, comply with regulations, and reduce costs.


