How to Address the Challenges in Web Guiding for Wider Webs Effectively
Table of Contents
In many industries, the need for wider webs include continuous rolls of material such as paper, plastic, textiles, or meta, has grown as manufacturers scale up production to meet higher demands. However, guiding wider webs through production processes presents unique challenges that require advanced web guiding system equipment to maintain accuracy and efficiency. In this article, we explore the critical aspects of web guiding for wider webs, including the common issues faced, effective solutions, and recent technological advancements making wide web guiding more efficient and precise.
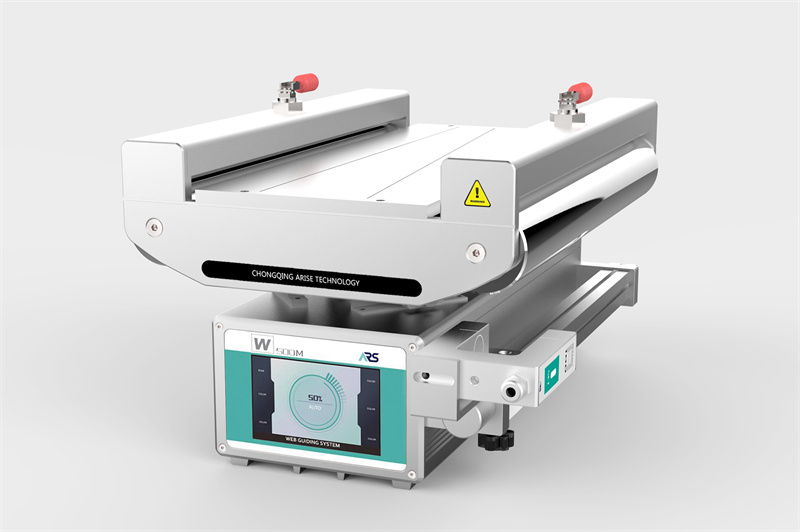
The Importance of Web Guiding for Wide-web Applications
Wide-web materials are used in various applications, including packaging, textiles, paper, and metal processing. As the width of a web increases, so does the potential for issues like misalignment, tension inconsistencies, and tracking errors. Effective web guiding systems are designed to keep the material centered and aligned, preventing defects and reducing waste. For wider webs, guiding systems must be highly responsive and adaptable to ensure that the material remains on course throughout each phase of production.
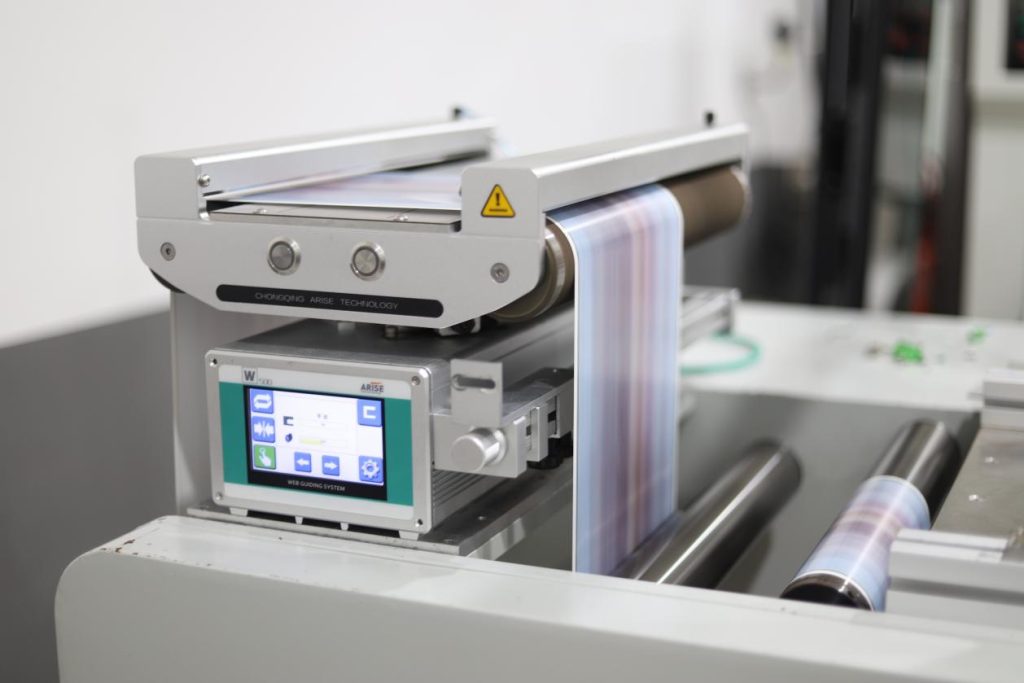

Challenges and Solutions in Web Guiding for Wider Webs
1. Greater Susceptibility to Tension Variability
For wider webs, maintaining consistent tension across the entire width is a crucial challenge. Unlike narrower webs, wider webs are more prone to tension fluctuations due to their increased surface area, which can cause the web to wander or misalign. This issue can lead to uneven winding, creasing, and in some cases, product damage.
Solution: Advanced tension control systems, such as load cells and sensors, are employed to continuously monitor and adjust the tension across the web width. Closed-loop control systems that actively adjust roller speed and tension at various points on the web are particularly effective for wider webs, ensuring a balanced tension distribution.
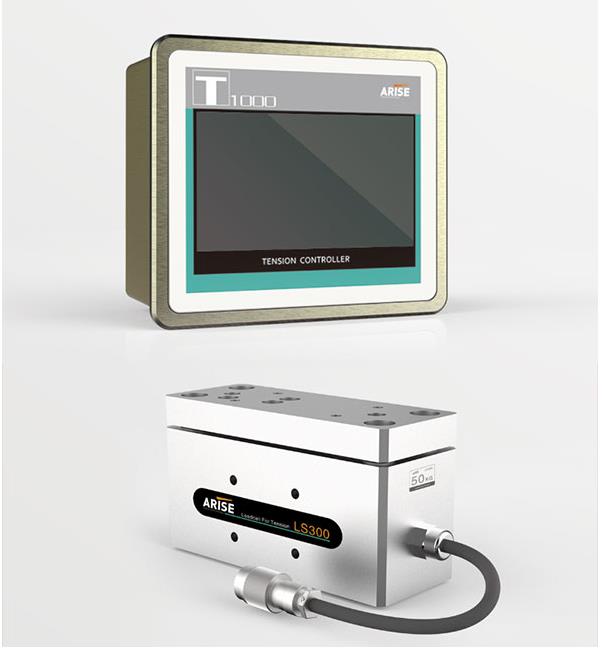
2. Roller Alignment and Stability
As the width of a web increases, so does the complexity of roller alignment and stability. Misalignment in rollers or minor vibrations can have a more pronounced effect on wider webs, resulting in tracking errors and material deformation. Maintaining alignment across multiple rollers is essential but can be difficult when managing increased widths.
Solution: Implementing precision-machined rollers and high-tolerance support structures can reduce alignment errors. Additionally, using dynamically adjustable guiding rollers that automatically realign based on sensor feedback helps to mitigate tracking issues. Precision in roller balancing also minimizes vibration, contributing to stable web travel.
3. Increased Demand on Web Guide Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators play a critical role in monitoring and adjusting web position. For wider webs, more sophisticated and higher-resolution web guide sensors are needed to accurately detect deviations across a larger surface area. The time it takes for actuators to correct deviations increases with the width, requiring high-speed, robust systems.
Solution: The latest web guiding systems for wider webs incorporate multi-sensor arrays that provide broader coverage and detect deviations across the entire width. Actuators designed for high-speed response are essential, and many systems use dual or multiple actuators to provide additional correction power for wider webs.
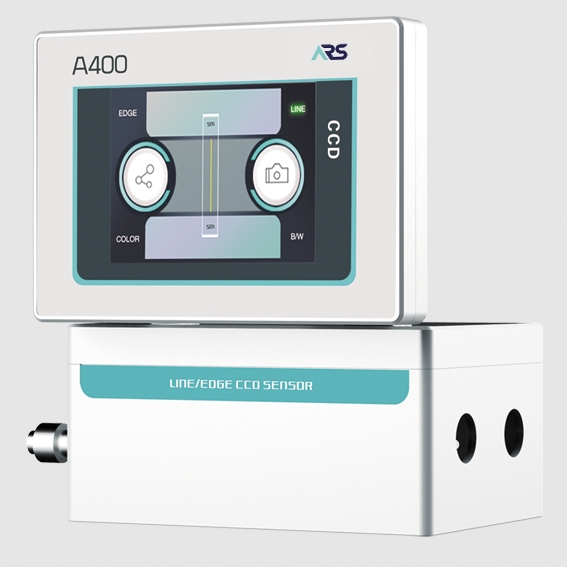

4. Sensitivity to Environmental Factors
Wider webs are more sensitive to environmental changes such as temperature and humidity, which can cause the material to expand, contract, or deform. This sensitivity can lead to tracking issues and impact product quality.
Solution: Environmental control systems, such as humidity and temperature sensors, are used to monitor conditions that may affect the web. Many facilities are now integrating climate control solutions in production areas, while advanced guiding systems have sensors that automatically adjust guiding parameters based on environmental changes.
5. Requirement for Customizable Web Path Control
The flexibility in web path control is often required in processes that involve multiple stages or have complex configurations, such as lamination and coating applications. For wider webs, managing the web path to meet specific production needs can be more complicated due to the web’s size and increased potential for path deviation.
Solution: Customizable, programmable web guide systems enable operators to set precise path requirements. Some advanced systems offer pre-set paths for specific applications, allowing for rapid configuration changes. These programmable systems can also adapt dynamically during production to ensure consistent alignment, even in complex, multi-stage processes.
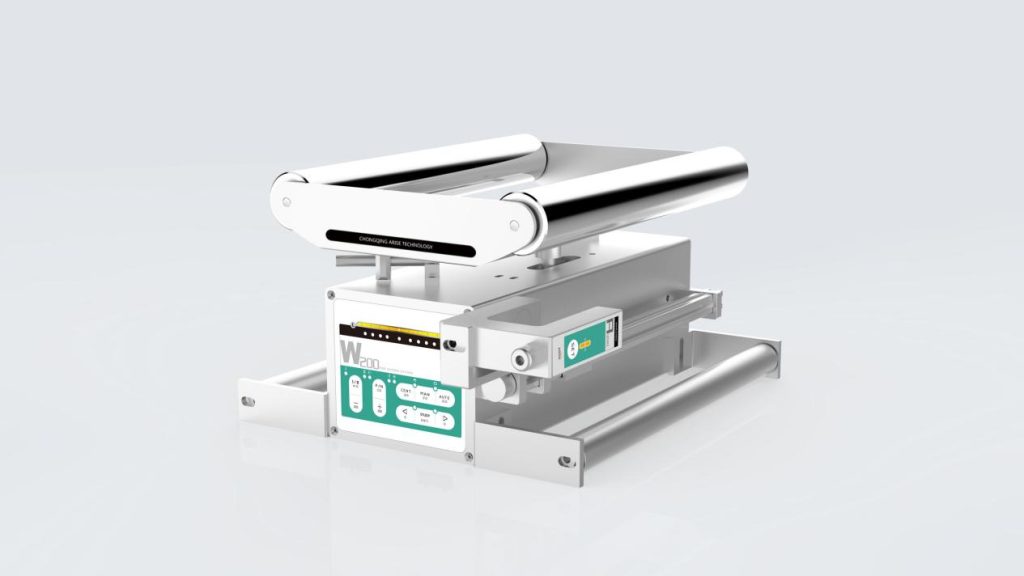

6. Potential for Increased Wear and Tear on Components
Handling the increased load associated with wider webs can accelerate wear on mechanical components, especially on rollers, actuators, and sensors. Wider webs require a robust system that can manage the additional forces without sacrificing longevity or requiring frequent maintenance.
Solution: For durability, selecting components made from high-strength, wear-resistant materials like hardened steel or specialized coatings can extend the lifespan of parts. Additionally, predictive maintenance tools that monitor the condition of web guiding components can help identify wear before it leads to breakdowns, ensuring smooth operation over time.
7. Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Wider webs demand more from the system, which can result in higher energy consumption. In a high-production environment, this increase can substantially affect operational costs.
Solution: Energy-efficient motors and actuators, often with variable speed control, are essential in minimizing energy consumption. Advanced power management solutions, such as regenerative drives that recycle energy back into the system, can also help offset the increased energy demand associated with wider webs.
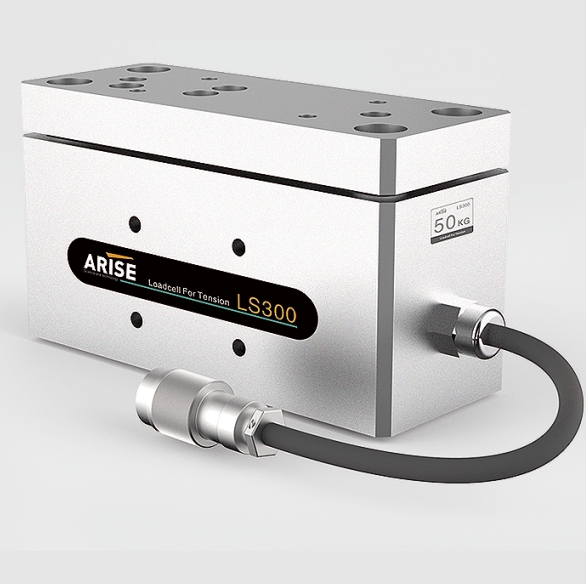

Technological Advances in Web Guiding for Wide-web Applications
Recent advancements in automation and digitalization have brought new solutions for guiding system in wide-web applications
| Technological Advance | Description | Benefits |
| Automated Tension Control Systems | Advanced load cell technology with closed-loop feedback for real-time tension adjustments across wide webs. | Maintains uniform tension, minimizes wrinkles and shifting. |
| Dynamic Roller Alignment with Anti-Vibration | Precision-aligned rollers equipped with anti-vibration mechanisms to reduce material drift. | Enhances stability and prevents misalignment across widths. |
| Multi-Sensor High-Resolution Arrays | Multiple sensors placed strategically across the web width to monitor alignment continuously. | Provides precise deviation detection, ensuring accuracy. |
| Environment-Adaptive Control | Integrated sensors for monitoring and adjusting to temperature, humidity, and static changes. | Compensates for environmental shifts, maintains quality. |
| Smart Actuators with Real-Time Feedback | Rapid-response actuators with feedback loops for immediate alignment adjustments. | Increases responsiveness, critical for high-speed webs. |
| AI-Powered Predictive Adjustment | Machine learning algorithms that optimize guiding based on historical and real-time data. | Reduces manual intervention, improves long-term accuracy. |
| IoT-Enabled Remote Diagnostics | IoT connectivity for remote monitoring, performance analysis, and proactive maintenance. | Facilitates troubleshooting, boosts uptime and efficiency. |
| Energy-Saving Variable-Speed Motors | Motors with energy-efficient, variable-speed controls and regenerative capabilities. | Cuts energy usage, lowers operational costs sustainably. |

In summary, web guiding for wider webs involves unique challenges that require specialized solutions to maintain precision, reducing waste, and ensuring high-quality output. Through advancements in tension control, sensor technology, predictive maintenance, digitalization, etc, manufacturers can now achieve more efficient and reliable guide system for wide webs .

