How to Address the Challenges in Food Packaging Printing Effectively
Food packaging printing stands at the intersection of creativity, functionality, and compliance, ensuring that products not only look appealing but also adhere to stringent safety standards.
From ensuring safety and regulatory compliance to maintaining quality and sustainability, food packaging printers must address numerous hurdles to deliver packaging that meets the demands of both consumers and regulatory authorities. In this article, we delve into the key challenges faced by the food packaging printing industry and explore innovative solutions to address them effectively.

Challenges in Food Packaging Printing
1. Regulatory Compliance
Perhaps the most significant challenge in food packaging printing is ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Different regions have varying regulations governing food contact materials, including the inks and substrates used in printing. These regulations aim to safeguard public health by preventing harmful substances from leaching into food products. Printers must stay abreast of these regulations and carefully select materials that meet the necessary safety criteria. Failure to comply can result in costly recalls, legal penalties, and damage to brand reputation.
2. Safety and Migration Concerns
Food packaging printing involves the use of inks and coatings that must not pose any risk to consumers. Ink components must be carefully chosen to minimize the potential for migration—the transfer of substances from the packaging into the food. This requires thorough testing to assess the safety and compatibility of inks with various packaging materials and food types. Additionally, printers must consider factors such as temperature, acidity, and moisture, which can influence the likelihood of migration.
3. Adherence to Brand Guidelines
While ensuring regulatory compliance and safety is paramount, food packaging printing also serves as a crucial branding tool. Printers must strike a balance between meeting regulatory requirements and fulfilling brand guidelines. This includes accurately reproducing brand colors, logos, and imagery while ensuring that the packaging remains visually appealing and informative. Achieving this balance requires advanced color management techniques, high-quality printing equipment, and skilled personnel capable of executing complex designs with precision.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability in food packaging printing. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of packaging materials and processes, prompting brands to adopt more eco-friendly solutions. Printers are tasked with finding sustainable alternatives to traditional packaging materials and inks, such as using recycled or biodegradable substrates and vegetable-based inks. However, balancing sustainability with other considerations like cost-effectiveness and performance remains a challenge.
5. Technical Limitations and Compatibility Issues
Printing on food packaging presents unique technical challenges due to the diverse array of packaging materials and formats. Different substrates, such as plastics, paperboard, and metals, require specialized printing techniques and inks to achieve optimal results. Additionally, the shape and surface texture of packaging containers can affect print quality and adhesion. Printers must possess the technical expertise to overcome these challenges and deliver consistent, high-quality results across various substrates and packaging formats.
6. Supply Chain Complexity
Food packaging printing is often part of a complex supply chain involving multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, converters, printers, and brand owners. Coordination among these stakeholders is essential to ensure timely production, quality control, and compliance with specifications. Any disruption or miscommunication within the supply chain can result in delays, errors, and increased costs. Therefore, effective collaboration and communication are critical for success in food packaging printing.

Solutions to Address the Challenges in Food Packaging Printing
1. Investment in Advanced Printing Technologies
Embrace state-of-the-art printing technologies such as digital printing, flexography, and offset printing. These technologies offer precise color management, high-resolution printing, and faster production speeds, improving overall efficiency and quality.
2. Regulatory Compliance Management
Establish robust regulatory compliance management systems to ensure adherence to food safety regulations and packaging standards. Stay updated on regulatory changes and work closely with regulatory experts to assess and mitigate compliance risks.
3. Quality Assurance Systems
Implement comprehensive quality assurance systems and printing inspection technologies to monitor print quality, detect defects, and ensure consistency. Automated inspection systems can identify issues in real-time, minimizing errors and reducing waste.
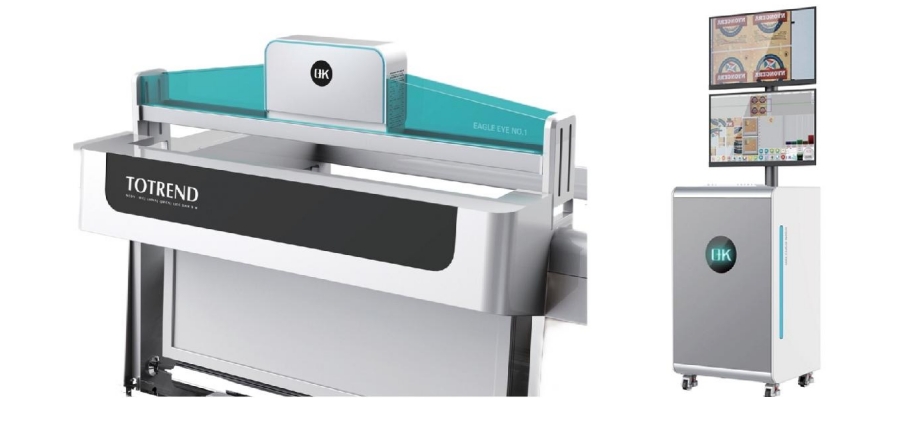

4. Sustainable Printing Practices
Embrace sustainable printing materials and processes to reduce environmental impact. Utilize eco-friendly substrates, biodegradable inks, and energy-efficient printing equipment to align with sustainability goals and meet consumer demand for eco-conscious packaging.
5. Collaboration Across the Supply Chain
Foster collaboration and communication among stakeholders in the food packaging supply chain, including material suppliers, converters, printers, and brand owners. Streamline workflows, share best practices, and leverage collective expertise to optimize processes and address challenges collaboratively.
6. Investment in Training and Skill Development
Provide ongoing training and skill development opportunities for printing personnel to enhance technical expertise, regulatory knowledge, and problem-solving abilities. Empower employees to identify and address challenges proactively, driving continuous improvement in printing practices.
7. Integration of Data Analytics and Automation
Leverage data analytics and automation tools to optimize printing processes, improve efficiency, and reduce errors. Analyze production data to identify trends, optimize workflows, and make data-driven decisions that enhance overall performance and quality.
8. Continuous Improvement Culture
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback, implementing feedback loops, and celebrating successes. Encourage innovation, experimentation, and collaboration to drive ongoing advancements in food packaging printing practices.
How Printing Inspection Systems are Used to Address the Challenges in Food Packaging Printing
1. Quality Control and Defect Detection
Printing inspection systems utilize advanced imaging technology to detect defects such as misprints, smudges, streaks, and color variations on printed packaging materials. By automatically scanning and analyzing printed substrates in real-time, these systems help identify and rectify quality issues before they escalate, ensuring that only flawless packaging reaches consumers.
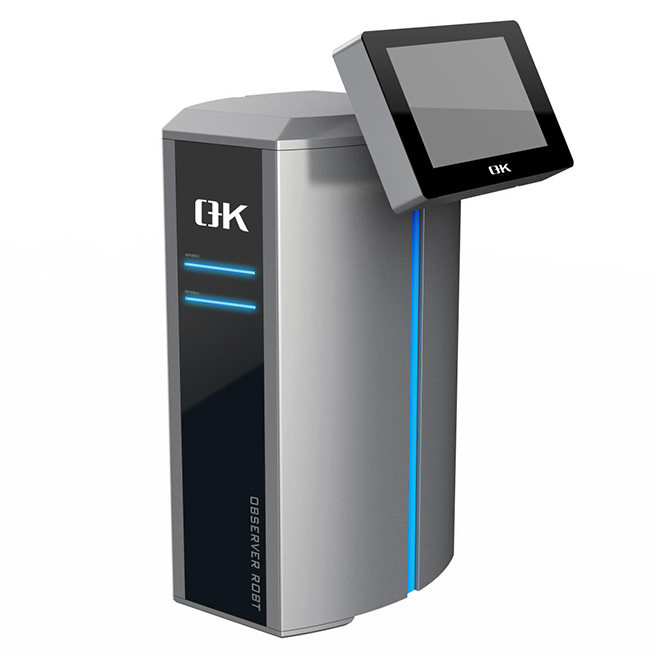

2. Color Consistency and Accuracy
Consistent color reproduction is essential for maintaining brand identity and ensuring consumer trust. Printing inspection systems employ color management algorithms to compare printed colors against reference standards and detect deviations. By monitoring color consistency throughout the printing process, these systems help printers achieve accurate and uniform color reproduction across different substrates, batches, and printing runs.

3. Barcode and Text Verification
Accurate printing of barcodes, expiration dates, batch codes, and other essential text is critical for traceability and regulatory compliance in the food industry. Printing inspection systems verify the readability and accuracy of printed text and codes using optical character recognition (OCR) and barcode verification algorithms. This ensures that all necessary information is legible and correctly printed on packaging materials, reducing the risk of errors and regulatory non-compliance.
4. Regulatory Compliance Assurance
Food packaging printing is subject to strict regulatory requirements governing ink migration, substrate suitability, and labeling. Printing inspection systems help ensure compliance with these regulations by detecting potential issues such as ink smudging, incomplete printing, or non-compliant materials. By providing objective evidence of compliance, these systems help mitigate the risk of regulatory penalties, product recalls, and reputational damage.
5. Data Integrity and Documentation
Printing inspection systems generate detailed reports and documentation of inspection results, including images, measurements, and timestamps. This documentation serves as a comprehensive record of print quality and compliance, enabling traceability and accountability throughout the printing process. By maintaining accurate records, printing inspection systems facilitate audits, investigations, and continuous improvement initiatives, enhancing transparency and confidence in the printing process.
5. Real-time Monitoring and Intervention
By integrating with printing equipment and production workflows, printing inspection systems enable real-time monitoring and intervention in response to detected issues. Automated alerts and notifications notify operators of potential problems, allowing them to take corrective action promptly. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces waste, and optimizes overall production efficiency, ensuring timely delivery of high-quality printed packaging materials.
6. Process Optimization and Continuous Improvement
Printing inspection systems provide valuable data and insights into printing performance, including defect trends, error rates, and production bottlenecks. By analyzing this data, printers can identify root causes of quality issues, implement corrective actions, and optimize printing processes for greater efficiency and reliability. Continuous improvement efforts driven by printing inspection systems help enhance print quality, reducing costs, and maintaining compliance with evolving regulatory standards.

Conclusion
Food packaging printing is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of regulatory requirements, safety concerns, quality control, sustainability, and collaboration across the supply chain. Through proactive measures, investments in technology, and a focus on sustainability and quality, the food packaging printing industry can continue to evolve and meet the ever-changing demands of consumers and regulatory authorities alike.


