How Automation Enhances Web Guide Systems across Various Industries
Web guide systems are critical in industries like printing, packaging, and textiles, where maintaining material alignment is essential for ensuring high-quality output and operational efficiency. Traditional manual adjustments in these systems are prone to errors and often result in wasted materials, downtime, and suboptimal production speeds. With advancements in technology, automation has revolutionized web guide systems, offering enhanced precision, real-time monitoring, and significant improvements in overall performance.

Table of Contents
What are Web Guide Systems
Web guide systems are used to control the lateral position (side-to-side movement) of continuous materials, or “webs,” as they move through processing equipment. These systems are essential in industries such as printing, packaging, converting, and textiles, where even minor misalignments can lead to defects, material waste, and production downtime. Traditional web guide systems rely on manual adjustments or basic mechanical controls, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
Automation has revolutionized web guide systems by introducing advanced sensors, actuators, and control algorithms that ensure precise alignment without the need for constant human intervention. Automated web guide systems are now a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling faster production speeds, higher accuracy, and improved operational efficiency.

The Role of Automation in Web Guide Systems
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback
Automated web guiding systems use advanced sensors and vision systems to monitor the position of the web in real-time. These sensors, which can include edge sensors, line sensors, or laser-based detectors, continuously track the web’s alignment as it moves through the production process. Vision systems equipped with cameras provide even more detailed feedback, enabling the detection of even the slightest misalignments. This real-time monitoring ensures that any deviations from the desired alignment are detected immediately, allowing for quick corrections and minimizing the risk of defects.
2. Precise and Rapid Adjustments
Once a misalignment is detected, automated web guide systems use actuators and servo motors to make precise adjustments to the position of rollers, guides, or frames. These components are highly responsive, enabling rapid corrections that maintain the web’s alignment with micron-level accuracy. The ability to make quick and precise adjustments ensures consistent product quality, even at high production speeds, and reduces material waste caused by misalignment.
3. Advanced Control Algorithms
Automated web guide systems are powered by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and sophisticated control algorithms. These algorithms analyze data from sensors and determine the optimal adjustments needed to maintain alignment. Some systems also incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to improve their performance over time, enabling predictive adjustments and adaptive control. Advanced algorithms enhance the system’s ability to handle complex or variable materials, ensuring reliable performance across a wide range of applications.
4. Reduced Human Intervention
Automation minimizes the need for manual adjustments, reducing the reliance on human operators. This not only lowers labor costs but also eliminates the potential for human error, ensuring more consistent and reliable operation. Reduced human intervention leads to higher operational efficiency and allows operators to focus on other critical tasks.
5. Integration with Broader Systems
Automated web guide systems can be integrated with other automated equipment and control systems within a production line. This integration enables seamless communication between machines, optimizing the entire production process and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Enhanced coordination and efficiency reduce downtime and improve productivity.
6. Enhanced Adaptability
Automated web guide systems are highly adaptable and can handle a wide range of materials, including thin films, delicate fabrics, and rigid metals. They can also be easily reprogrammed to accommodate different production requirements, making them suitable for diverse industries and applications. This enhanced adaptability allows manufacturers to use the same system for multiple products or processes, reducing the need for specialized equipment.
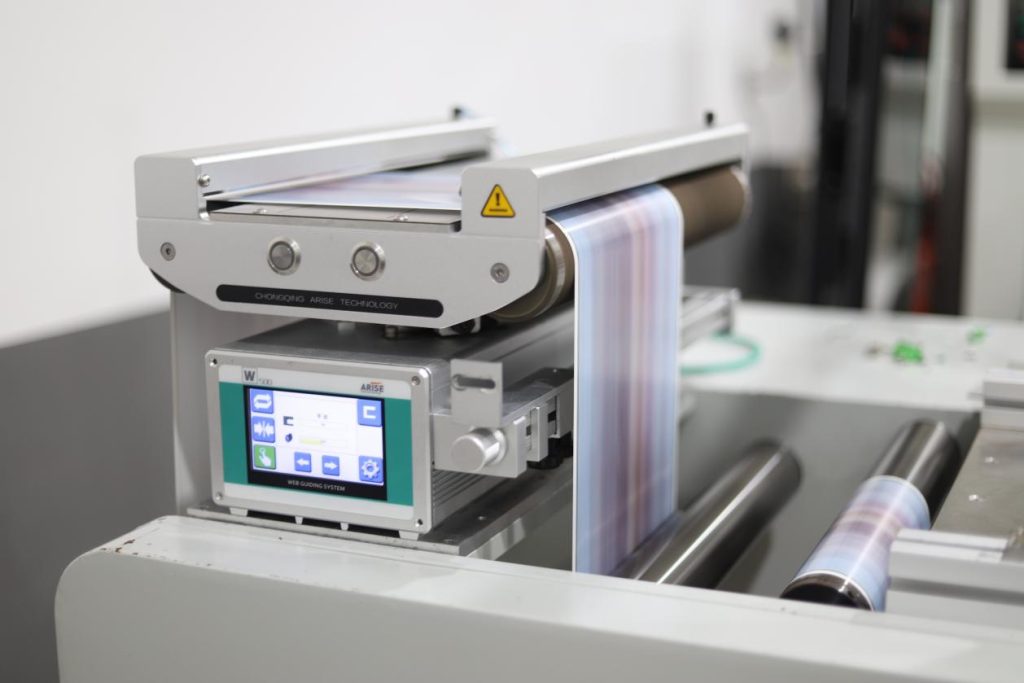

7. Improved Data Collection and Analysis
Automated systems collect vast amounts of data on web alignment, production speeds, and system performance. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize processes, and predict potential issues before they occur. Improved data collection and analysis enable proactive maintenance and continuous process improvement, further enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
8. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
By maintaining precise alignment, automated web guide systems minimize material waste caused by edge trim, web breaks, or jams. This not only reduces costs but also contributes to more sustainable manufacturing practices. Reduced material waste and improved efficiency support environmental sustainability and align with global efforts to reduce industrial waste.
9. User-Friendly Interfaces
Automated web guide systems often feature human-machine interfaces (HMIs) with touchscreen displays and intuitive software. These interfaces make it easy for operators to monitor system performance, make adjustments, and troubleshoot issues. User-friendly interfaces in web guiding equipment simplify operation and reduce the learning curve for new operators, ensuring smooth implementation and operation.
Key Components of Automated Web Guide Systems
This chart highlights the essential components of an automated web guide system and their functions.
| Component | Description |
| Sensors | Detect the position and alignment of the material (web). Common types include infrared, laser, or vision sensors. |
| Actuators | Adjust the position of the web in response to sensor data, ensuring proper alignment. |
| Guide Controller | The central processing unit that analyzes sensor feedback and sends commands to actuators for adjustments. |
| Guiding Mechanism | The physical structure (rollers, rollers with friction, or air jets) that physically steers the web into place. |
| Drive System | Provides the motion needed to control rollers or other parts of the system to move the web correctly. |
| User Interface (HMI) | Allows operators to monitor system performance and make adjustments as needed, providing data and diagnostics. |
| Feedback Loop | A closed-loop system that ensures constant real-time monitoring and adjustments, maintaining web alignment. |
| Communication System | Facilitates communication between the web guide system and other equipment in the production line for synchronized operation. |
| Diagnostic Tools | Built-in monitoring tools for system health, predictive maintenance, and identifying potential issues. |
| Power Supply | Provides electrical energy to power all system components, including actuators, sensors, and controllers. |
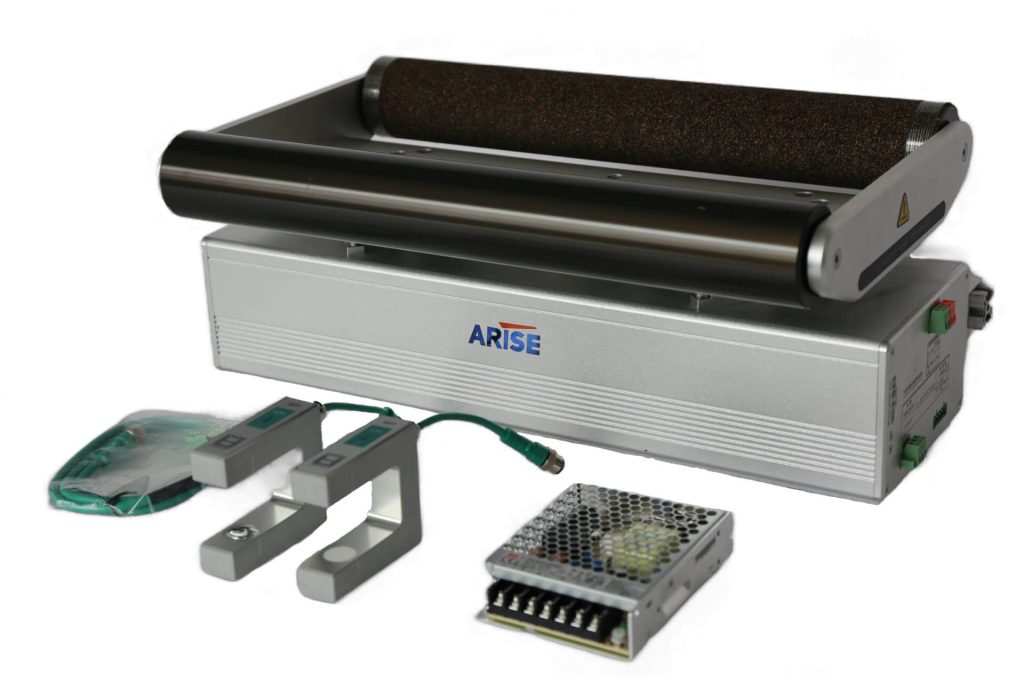

Applications of Automated Web Guide Systems
- Printing and Packaging
Automated web guide systems ensure that printed materials are perfectly aligned, preventing misprints and reducing material wastage. In flexible packaging, where accuracy is crucial for product integrity and branding, these systems maintain the correct positioning of films and laminates, ensuring smooth and error-free production.
- Paper and Tissue Industry
Another significant area of application is the . In high-speed paper production lines, web guide systems control the position of continuous paper rolls, preventing wrinkles, misalignment, or edge damage. This level of precision is vital for producing high-quality finished products such as newspapers, magazines, and packaging materials.
- Textile and Non–woven Industries
Automated web guide systems are used to maintain fabric alignment during processes like dyeing, coating, and laminating. Accurate guiding reduces defects and ensures consistent product quality across large-scale production. This is especially important for industries producing medical textiles, automotive fabrics, and other technical textiles where uniformity is critical.
- Converting Industry
During the slitting, rewinding, or coating of materials such as plastic films and foil, these systems ensure accurate alignment to avoid product defects. This is particularly essential for industries involved in the production of adhesive tapes, labels, and industrial films where precision and repeatability are mandatory.
- Metal Processing Sector
Automated web guide systems are widely used in the . In metal coil handling, these systems guide sheets and strips through cutting, coating, or stamping processes. Proper alignment minimizes material waste and improves product consistency, which is critical for automotive, aerospace, and construction applications.
- The Pharmaceutical and Medical Industries
Automated web guide systems are widely used in the production of medical packaging and disposable products. Accurate web guiding ensures that sterile materials remain uncontaminated while maintaining tight tolerances during manufacturing. This is essential for meeting stringent regulatory standards.

Challenges and Future Trends in Automated Web Guide Systems
This chart provides a clear view of current challenges in automated web guides alongside the evolving trends that aim to address these issues in the future.
| Category | Challenges | Future Trends |
| Precision Control | – Difficulty in maintaining precise tension control in high-speed operations. | – Advanced sensors and AI for real-time monitoring and automated adjustments. |
| Environmental Factors | – Variability in ambient conditions (temperature, humidity) affecting system performance. | – Integration of adaptive control systems that adjust to environmental changes in real-time. |
| Integration with Other Systems | – Challenges in integrating with existing production lines and machinery. | – Seamless integration with Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and cloud-based analytics. |
| Maintenance and Reliability | – Regular wear and tear of mechanical components leading to frequent downtime. | – Predictive maintenance using machine learning algorithms to reduce unexpected failures. |
| Material Variability | – Difficulty in adjusting the system for different materials with varying properties. | – Multi-material compatibility with intelligent web guiding systems that automatically adjust settings. |
| Cost Efficiency | – High initial investment and operational costs. | – Cost reduction through automation, digitalization, and more efficient system designs. |
| System Complexity | – Complex calibration and setup processes for optimal performance. | – Simplified user interfaces and auto-calibration features to reduce setup time and complexity. |
| Energy Consumption | – High energy consumption in traditional systems. | – Development of energy-efficient designs, including regenerative braking systems. |
| Data Analytics | – Limited data capture for predictive insights and performance optimization. | – Enhanced data analytics and machine learning models for proactive optimization of web guiding. |

Final Thoughts
Automation has transformed web guide systems from simple mechanical devices into highly sophisticated, intelligent systems that enhance precision, efficiency, and reliability in industrial processes. Through adopting real-time monitoring, advanced control algorithms, and seamless integration with broader systems, automated web guiding control systems are helping manufacturers achieve higher product quality, reduce waste, and improve operational efficiency. Automation not only enhances the functionality and performance of web guide systems but also empowers manufacturers to maintain competitiveness in rapidly evolving markets.


