Energy-Efficient Tension Control Solutions: Maximizing Efficiency
Optimizing energy consumption is paramount for sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Among the myriad of processes, tension control stands out as a critical aspect in various manufacturing operations. Whether in the web handling, printing, packaging, or textile sectors, exact tension levels are critical for product quality and operational efficiency. However, traditional tension control mechanisms often consume significant amounts of energy. To address this challenge, industries are increasingly turning towards energy-efficient tension control solutions.

Why Select Energy-Efficient Tension Control
Understanding the Basics of Tension Control
| Aspect | Description |
| Definition | Tension control is a process used to regulate and maintain the tension of a material, such as a web or a wire, during processing. |
| Purpose | The primary purpose of tension control is to ensure uniform tension across the material, preventing wrinkles, tears, or breaks. |
| Components | Tension control systems typically consist of components such as tension sensors, tension controllers, actuators, and feedback mechanisms. |
| Types | Common types of tension control systems include open-loop control, closed-loop control, and dancer control systems. |
| Measurement | Tension is measured using tension sensors or load cells, which detect the force exerted on the material as it passes through the system. |
| Control Mechanism | Tension control systems adjust tension by modulating the speed or torque of motors, brakes, clutches, or rollers in the process line. |
| Applications | Tension control is used in various industries, including paper manufacturing, printing, packaging, textile processing, and wire and cable production. |
| Benefits | The benefits of tension control include improved product quality, increased production efficiency, reduced waste, and extended equipment lifespan. |
| Challenges | Challenges associated with tension control include achieving precise tension control, minimizing material waste, and maintaining system reliability. |
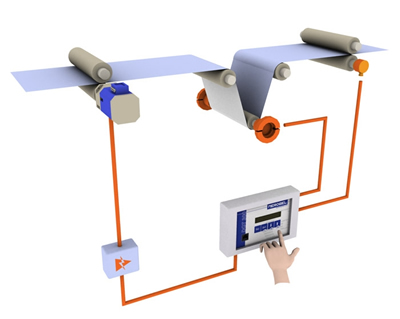
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Tension Control Solutions for Industrial Operations
- Cost Savings
Energy-efficient tension control solutions can dramatically cut energy usage, lowering utility bills and operating costs. Businesses that optimize their energy usage can enhance their bottom line and utilize resources more efficiently.
- Environmental Sustainability
Energy efficiency is closely linked to environmental sustainability. By reducing energy consumption, businesses can lower their carbon footprint and contribute to mitigating climate change. Choosing energy-efficient tension control solutions demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility and corporate citizenship.
- Compliance with Regulations
Many regions have stringent regulations and standards regarding energy usage and environmental impact. By adopting energy-efficient technologies, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential penalties or fines. Additionally, demonstrating adherence to sustainability initiatives can enhance brand reputation and market competitiveness.
- Enhanced Equipment Performance
Energy-efficient tension control solutions often incorporate advanced technologies and intelligent algorithms to optimize system performance. By maintaining precise tension levels and minimizing energy waste, these solutions can improve equipment reliability, longevity, and overall operational efficiency.
- Improved Product Quality
Consistent tension control is essential for maintaining product quality and integrity, especially in industries such as printing, packaging, and textiles. Energy-efficient tension control solutions ensure uniform tension levels, reducing the risk of product defects, waste, and rework. This, in turn, enhances customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Flexibility and Adaptability
Energy-efficient tension control solutions are often designed to be versatile and adaptable to varying production requirements and process conditions. Whether it’s adjusting tension levels for different materials, speeds, or environmental factors, these solutions offer flexibility and customization options to meet specific operational needs.
- Future-Proofing Investments
Investing in energy-efficient solutions not only results in immediate cost savings, but also protects businesses from growing energy bills and changing regulatory requirements. Prioritizing energy efficiency enables organizations to secure the durability and sustainability of their operations in the face of changing market circumstances.
Innovative Approaches in Energy-Efficient Tension Control Solutions
1. Regenerative Braking Systems
Traditional tension control systems frequently employ mechanical brakes or clutches to manage tension. However, upon braking, these systems waste energy as heat, resulting in energy loss. In contrast, regenerative braking systems absorb and store this energy for later utilization.By employing regenerative drives or mechanisms, excess kinetic energy generated during braking is converted into electrical energy, which can be stored in batteries or capacitors and reused within the system. This approach not only reduces energy consumption but also helps in managing peak power demands more efficiently.
2. Intelligent Control Algorithms
Incorporating intelligent tension control algorithms into tension control systems allows for real-time monitoring and adjustment of tension levels based on variables such as material type, speed, and environmental conditions. These algorithms dynamically optimize tension control parameters, resulting in the most energy-efficient operation while maintaining optimal tension levels. Intelligent control systems reduce energy waste by continuously assessing data from sensors and feedback mechanisms.
3. Low-Friction Components
Friction within tension control components such as rollers, bearings, and guides can significantly impact energy consumption. Utilizing low-friction materials, coatings, and design optimizations helps reduce frictional losses and energy requirements. By minimizing resistance and improving the smoothness of material movement, low-friction components contribute to energy efficiency while extending the lifespan of equipment.
4. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
VFDs are widely used in industrial applications to control the speed of electric motors. In tension control systems, VFDs enable precise adjustment of motor speeds based on process requirements, resulting in energy savings. By matching motor speed to the required tension level, VFDs eliminate energy wastage associated with constant-speed operation. Additionally, VFDs offer features such as soft-start functionality, which reduces mechanical stress on equipment and further enhances energy efficiency.
5. Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring
Implementing predictive maintenance techniques and condition monitoring systems helps identify potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. By regularly monitoring the condition of tension control equipment and analyzing performance data, manufacturers can schedule maintenance activities more effectively, optimize system efficiency, and prevent energy losses due to unexpected downtime or malfunctions.
6. System Integration and Optimization
Integrating tension control systems with broader energy management platforms allows for comprehensive optimization of energy usage across manufacturing processes. By synchronizing tension control operations with other energy-intensive equipment and processes, manufacturers can implement coordinated energy-saving strategies. This holistic approach involves real-time data monitoring, analysis, and optimization to maximize energy efficiency and overall productivity.
Conclusion
Energy-efficient tension control solutions provide an appealing opportunity for enterprises to improve operations while reducing environmental impact. By employing innovative technology, intelligent algorithms, and integrated energy management systems, factories can achieve significant energy savings and improve overall productivity and sustainability.


