Edge vs. Center Web Guide Systems: Which Type to Choose
Web guide systems are critical in ensuring that materials such as paper, film, foil, and textiles are properly aligned as they move through various stages of production. Among the various types, edge web guide systems and center web guide systems are the two most commonly used solutions. The selection between edge vs. center web guide systems, depends on material properties, application requirements, process precision, cost, etc. This article provides a comparative analysis of both systems, highlighting their working principles, advantages and best-use scenarios.

Table of Contents
What are Edge Web Guide Systems
In web-based manufacturing and processing industries, maintaining precise alignment of moving materials is crucial to ensuring product quality and process efficiency. Edge web guide systems play a key role in this by automatically detecting and correcting the lateral position of a web material, such as paper, film, textiles, or metal, as it moves through production lines. These systems help prevent misalignment issues that can lead to material waste, defective products, and costly downtime.
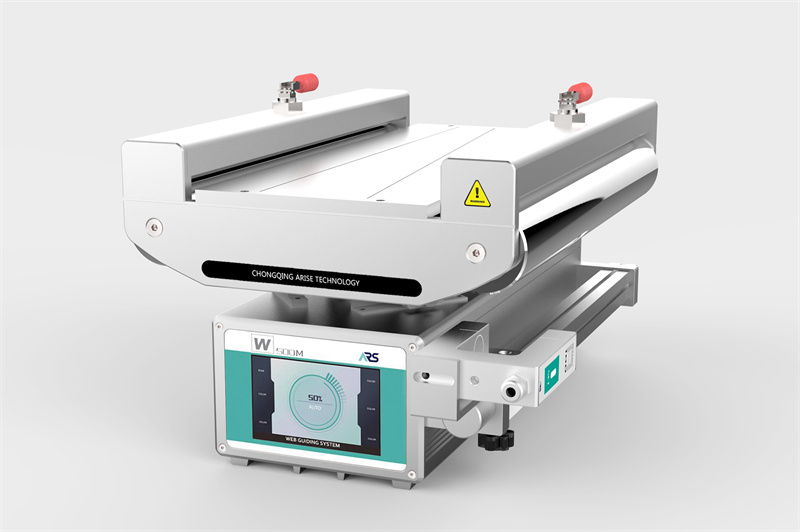
How them Work
Web edge guide systems operate by continuously monitoring the position of the web’s edge and making real-time adjustments to keep it aligned with a set reference. The system consists of three main components: sensors, controllers, and actuators.
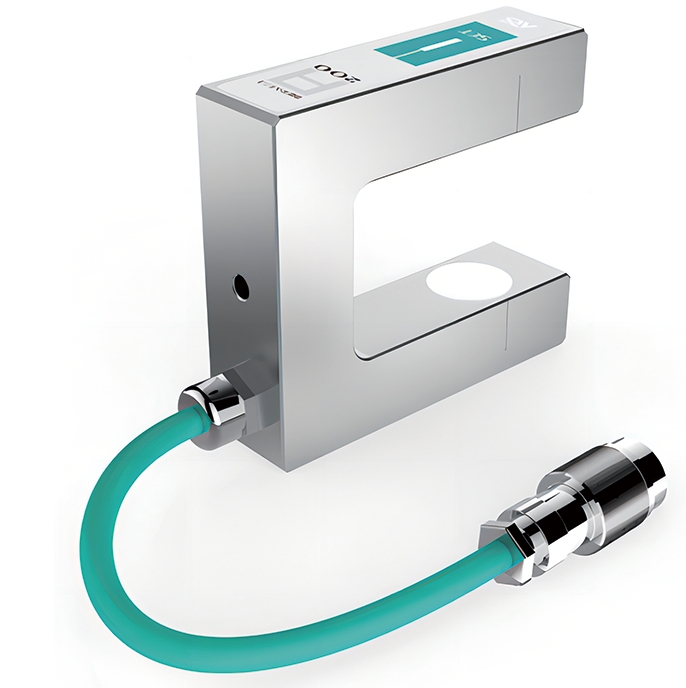
- Edge guiding sensors detect the position of the web edge using various technologies, such as ultrasonic, infrared, or optical sensors. Ultrasonic edge guide sensors are commonly used for non-transparent materials, while optical sensors work well for clear films and foils.
- The web guide controller receives data from the sensor and determines whether the web is misaligned. If necessary, it sends a correction signal to the actuator.
- The web guide actuator moves the guiding mechanism—such as rollers, steering frames, or a moving guide frame—to reposition the web and bring its edge back into alignment.
This continuous feedback loop ensures that the web remains in the correct position, even if external factors like tension variations or material inconsistencies cause deviations.

Applications
- Printing and Converting: Ensuring that images and text align correctly on packaging materials, labels, and newspapers.
- Slitting and Cutting: Keeping the material edge in the correct position for accurate trimming and minimizing waste.
- Coating and Laminating: Ensuring uniform application of coatings and adhesives on flexible materials.
- Textile and Film Processing: Preventing wrinkles and distortion by maintaining a straight edge during high-speed production.

Advantages
- Improved Accuracy: By keeping the web edge aligned, these systems help achieve precise printing, cutting, and coating applications.
- Reduced Waste: Proper alignment minimizes material defects, leading to lower scrap rates and cost savings.
- Increased Speed and Efficiency: Automation allows for high-speed operation without the need for manual adjustments.
- Compatibility with Various Materials: Works with a wide range of flexible materials, including paper, plastic, metal, and textiles.
- Easy Integration: Can be installed on existing production lines without major modifications.
What are Center Web Guide Systems
Center web guide systems are automated alignment systems designed to keep the moving web material centered as it passes through processing equipment. Unlike edge web guide systems, which align based on a single edge, center web guide systems maintain the web’s position relative to its centerline. This ensures balanced alignment, making them ideal for symmetrical processes like coating, laminating, and slitting, where both edges need to be evenly positioned.
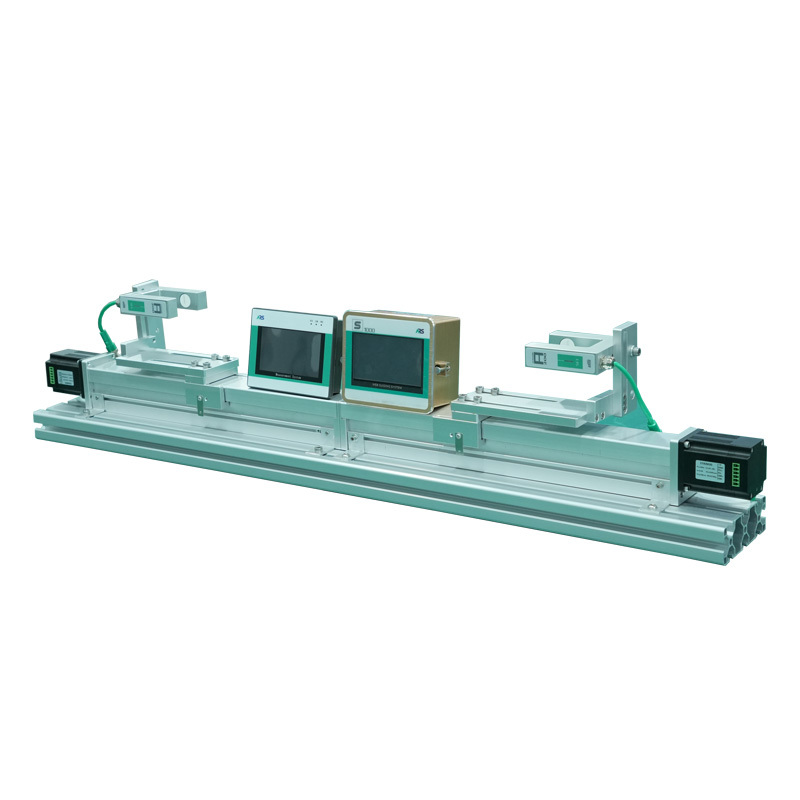

How them Work
A centering web guide system continuously monitors and adjusts the web’s position using dual sensors, a controller, and an actuator.
- Dual Sensors: These sensors (optical, infrared, or ultrasonic) detect both edges of the web and determine its center position.
- Controller: The control unit receives signals from the sensors and calculates whether the web is off-center.
- Actuator: If misalignment is detected, the actuator moves the web guiding mechanism (such as a moving guide frame or rollers) to realign the material and keep it centered.

This real-time correction prevents unwanted shifts and ensures consistent alignment, even if the web width varies due to trimming or tension fluctuations.
Applications
- Laminating and Coating: Ensures even application of adhesives and coatings on both sides.
- Slitting and Trimming: Maintains proper positioning for equal trimming of both edges.
- Printing and Converting: Keeps printed patterns aligned for symmetrical designs.
- Film and Flexible Packaging: Prevents uneven stretching or distortion of materials.
Advantages
- Uniform Alignment: Ensures both edges are evenly positioned, critical for symmetrical applications.
- Reduced Edge Variation Issues: Accommodates materials with slight edge inconsistencies.
- Ideal for Varying Web Widths: Automatically adjusts for minor width variations.
- Improved Process Stability: Prevents material shifting that could lead to defects or waste.
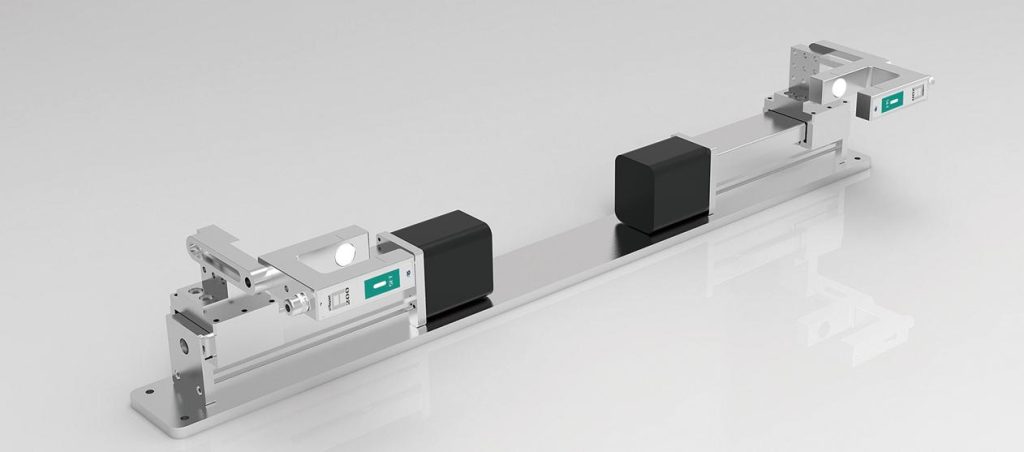
Comparison of Edge vs. Center Web Guide Systems
| Feature | Edge Web Guide System | Center Web Guide System |
| Alignment Method | Aligns based on a single edge | Aligns based on the centerline of the web |
| Sensor Requirement | Single sensor detects one edge | Dual sensors detect both edges to find the center |
| Best For | Applications where one edge must stay fixed | Applications requiring symmetrical alignment |
| Adaptability to Web Width Changes | Less adaptable; assumes a fixed edge position | More adaptable; automatically adjusts to width variations |
| Complexity of System | Simpler system with fewer components | More complex due to dual sensors and precise centering control |
| Ideal for High-Speed Processes | Yes, but primarily for applications where only one edge needs correction | Yes, especially when uniform processing is required |
| Cost | Generally lower due to fewer components | Higher due to additional sensors and control complexity |
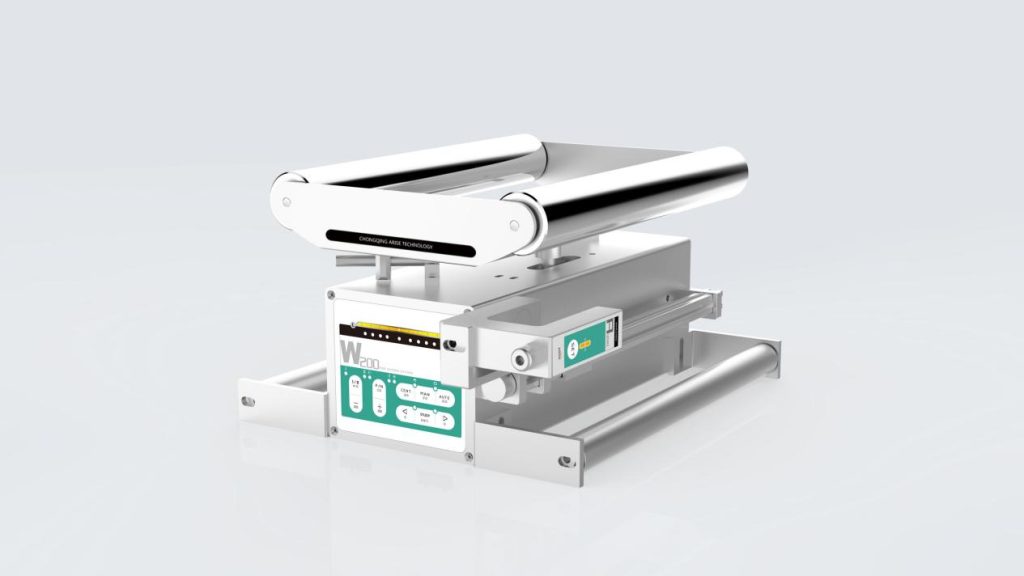

Key Factors to Consider for Choosing Between Edge vs. Center Web Guide Systems
| Factor | Edge Web Guide System | Center Web Guide System |
| Type of Web Material | Suitable for materials with a consistent edge (paper, metal foils, rigid films) | Ideal for materials with varying edge quality (stretchable films, textiles) |
| Web Width Variation | Best for fixed-width webs | Adapts to width fluctuations |
| Required Alignment Precision | Provides good accuracy but only for single-edge correction | Offers high precision by balancing both edges |
| Type of Processing Application | Used in printing, edge slitting, and coating where one edge must stay fixed | Preferred for laminating, precise slitting, and dual-sided coating requiring symmetrical alignment |
| Cost and System Complexity | Lower cost, simpler sensor setup | Higher cost due to dual sensors and advanced control mechanisms |
| Speed and Production Efficiency | Works efficiently at high speeds but may need manual adjustments for width changes | Maintains consistent centering at high speeds, reducing material waste |
| Waste Reduction and Material Utilization | Reduces waste on one side but may cause misalignment if width changes | Minimizes waste by ensuring even material distribution on both edges |
Summary
- Edge web guiding is often preferred for applications where one edge must remain fixed.
- Center web guiding is better suited for processes that require balanced alignment, such as symmetrical laminating or slitting.

Final Thoughts
Choosing between edge and center web guide systems depends on the nature of the web material and the specific processing requirements. Understanding the differences and benefits of each system ensures optimal material handling, reduced waste, and improved production efficiency.


